Lecture
A gyroscope (or a top) is called a massive symmetric body, rotating at high speed around the axis of symmetry (Fig.5.5).
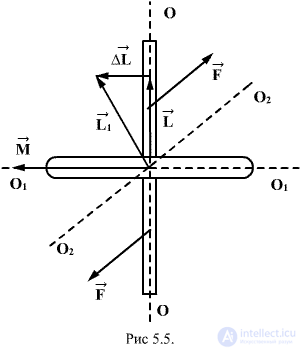
The moment of the momentum of the gyroscope coincides with its axis of rotation. In order to change the direction in space of the axis of the gyroscope, i.e. vector direction 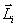 necessary in accordance with the basic equation of the dynamics of rotational motion
necessary in accordance with the basic equation of the dynamics of rotational motion  act upon it with a moment of external forces
act upon it with a moment of external forces 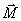 . Let it be a couple of forces
. Let it be a couple of forces 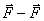 creating torque about the axis
creating torque about the axis 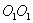 lying in the plane of the drawing perpendicular to the axis of the OO (rotation around
lying in the plane of the drawing perpendicular to the axis of the OO (rotation around 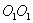 ). In this case, there is the following phenomenon, called the gyroscopic effect: under the action of a pair of forces, which, it would seem, should have caused the rotation of the axis of the gyroscope OO around the axis
). In this case, there is the following phenomenon, called the gyroscopic effect: under the action of a pair of forces, which, it would seem, should have caused the rotation of the axis of the gyroscope OO around the axis 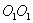 the axis of the gyro rotates around a straight line
the axis of the gyro rotates around a straight line 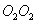 perpendicular to these axes (i.e., OO and
perpendicular to these axes (i.e., OO and 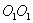 ). At first glance, the gyroscope’s “unnatural” behavior turns out to be completely consistent with the laws of the dynamics of the rotational motion, i.e ultimately, Newton's laws. Consider the behavior of the gyroscope under the action of the moment of force
). At first glance, the gyroscope’s “unnatural” behavior turns out to be completely consistent with the laws of the dynamics of the rotational motion, i.e ultimately, Newton's laws. Consider the behavior of the gyroscope under the action of the moment of force 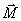 acting along the axis
acting along the axis 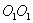 . During
. During 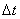 gyro moment of momentum
gyro moment of momentum 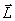 increment
increment 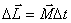 which has the same direction as
which has the same direction as 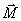 . The moment of the momentum of the gyroscope after time
. The moment of the momentum of the gyroscope after time 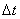 will be equal to the resultant
will be equal to the resultant 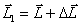 lying in the plane of the drawing. Vector direction
lying in the plane of the drawing. Vector direction 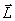 coincides with the new direction of the axis of rotation of the gyroscope. Thus, the axis of the gyro will rotate around the axis
coincides with the new direction of the axis of rotation of the gyroscope. Thus, the axis of the gyro will rotate around the axis 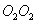 (perpendicular to the plane of the drawing), and so that the angle between the vectors
(perpendicular to the plane of the drawing), and so that the angle between the vectors 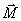 and
and 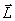 decreases: If a gyroscope acts for a long time with a constant in the direction of the moment of external forces, then the axis of the gyroscope is finally set so that the axis and direction of proper rotation coincide with the axis and direction of rotation under the action of external forces (vector
decreases: If a gyroscope acts for a long time with a constant in the direction of the moment of external forces, then the axis of the gyroscope is finally set so that the axis and direction of proper rotation coincide with the axis and direction of rotation under the action of external forces (vector 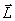 , coincides in direction with the vector
, coincides in direction with the vector 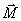 ).
).
Comments
To leave a comment
Physical foundations of mechanics
Terms: Physical foundations of mechanics