The history of computer games begins in 1947 and covers six decades. Part of the pop culture of the game began in the late 1970s.
Content
- 1 Chronology of events by year
- 2 Until 1940
- 3 1940–1950
- 4 1951–1960
- 5 1961–1970
- 6 1971-1980
- 6.1 1971
- 6.1.1 Arcade machines
- 6.1.2 Games
- 6.2 1972
- 6.2.1 Companies
- 6.2.2 Game Consoles
- 6.2.3 Arcade machines
- 6.3 1973
- 6.3.1 Companies
- 6.3.2 Arcade machines
- 6.3.3 Games
- 6.4 1974
- 6.4.1 Companies
- 6.4.2 Arcade machines
- 6.4.3 Games
- 6.5 1975
- 6.5.1 Companies
- 6.5.2 Microprocessors
- 6.5.3 Game Consoles
- 6.5.4 Games
- 6.6 1976
- 6.6.1 Companies
- 6.6.2 Microprocessors
- 6.6.3 Arcade machines
- 6.6.4 Game Consoles
- 6.7 1977
- 6.7.1 Computers
- 6.7.2 Arcade machines
- 6.7.3 Game Consoles
- 6.7.4 Games
- 6.8 1978
- 6.8.1 Companies
- 6.8.2 Arcade machines
- 6.8.3 Game Consoles
- 6.9 1979
- 6.9.1 Computers
- 6.9.2 Games
- 6.9.3 Arcade machines
- 6.9.4 Companies
- 6.9.5 Portable Game Consoles
- 6.10 1980
- 6.10.1 Companies
- 6.10.2 Computers
- 6.10.3 Arcade machines
- 6.10.4 Game Consoles
- 6.10.5 Portable Game Consoles
- 6.10.6 Games
- 7 1981–1990
- 7.1 1981
- 7.2 1982
- 7.3 1983
- 7.4 1984
- 7.5 1985
- 7.6 1986
- 7.7 1987
- 7.8 1988
- 7.9 1989
- October 7, 1990
- 8 1991-2000
- 8.1 1991
- 8.2 1992
- 8.3 1993
- 8.4 1994
- 8.5 1995
- 8.6 1996
- 8.7 1997
- 8.8 1998
- 8.9 1999
- 8.10 2000
- 9 2001—2010
- 9.1 2001
- 9.2 2002
- 9.3 2003
- 9.4 2004
- 9.5 2005
- 9.6 2006
- 9.7 2007
- 9.8 2008
- 9.9 2009
- October 9, 2010
- 10 2011–2020
- 10.1 2011
- 10.2 2012
- 10.3 2013
Chronology of events by year
Below is a chronology of events in the world of computer games by year. Each page tells about what a particular year entered the history of games.
Until 1940
1889 - Fusadziro Yamauchi founded the gaming company Marufuku for the production and sale of playing cardsHanafuda, which in 1907 was renamed Nintendo Koppai, which later became the largest company in the world among manufacturers of interactive entertainment [1] [2] .
1940-1950
1947 - Rocket simulator - the first known entertainment tool, similar to a computer game [3] .
1948-1950 - Alan Turing and David Champerun (Eng.) Russian. developed a chess game algorithm [4] . At that time there was not a powerful enough computer to execute this algorithm [5] .
March 1950 - Claude Shannon developed a chess program, which appeared in the article "Programming computer chess games", published in Physicosophical Magazine. This was the first article about the problem of computer chess.
1951–1960
The invention of computer games is usually attributed to one of three people: Ralph Baer, the engineer who put forward the idea of interactive television in 1951, A. S. Douglas, who wrote OXO in 1952, the computer implementation of the tic-tac-toe, or William Higinbotham, who created in the 1958 game "Tennis for Two".
1961-1970

Spacewar game!

Brown box
April 1962 - Spacewar! for PDP-1.
1965 - Rosen Enterprises and Service Games of Japan announced a merger, which resulted in the formation of Sega Enterprises.
1966 - The first text-based bingo game simulator, created by Larry Beturum for the PDP-10 computer. The programming language is BASIC, the size of the source code is 203 lines. Date of creation: January 23, 1966. [6]
In 1967:
- The first text-based basketball simulator created by Charles R. Bacheller for the PDP-10 computer. The programming language is BASIC, the size of the source code is 115 lines. [7]
- A baseball text simulator (“1967 World Series”) created by Jacob Bergmann for the PDP-10 computer. The programming language is BASIC, the size of the source code is 886 lines. [7]
In 1968:
- Doug Diment creates the first version of the game Hamurabi (originally called The Sumer Game) in Fokal. Hamurabi is considered the first known implementation of a town-planning simulator.
- On January 15, 1968, Ralph Baer received the first video game patent. In the same year, he completed the creation of the Brown Box, a device that was a prototype of the first-generation game console (Pong class game).
In 1969:
- March 21, 1969 Kajemas Kozuki founded a company selling, repairing and tuning jukeboxes. Later this company (already as Konami) became a leading manufacturer of arcade machines and computer games.
- Ralph Baer [en] signs a contract with Magnavox for the development of a game console.
- Ken Thompson has developed a Space Travel game that simulates a journey through the Solar System. Originally, Ken Thompson developed the game for the Multics operating system, and then he, together with other well-known programmer Dennis Ritchie, ported the game to the PDP-7 computer. [eight]
- Jim Storer (Jim Storer) developed the game Lunar Lander (Rus. Lunar "descent vehicle") - a text game, a simulator of landing the descent vehicle on the surface of the Moon. The player must save fuel and plant the machine at a low speed so as not to break the machine. The game is designed for the PDP-8 computer in the FOCAL programming language. The original name of the game was Lunar. [eight]
In 1970:
- Douglas Engelbart received a patent for a "display system XY position on the monitor," or, more simply, a computer mouse.
- developed a text game Highnoon (Rus. "Exactly at Noon"), a duel simulator on pistols from the times of the Wild West. The opponent of the game is the character of the famous 19th century gangster Black Bart. The game begins 100 paces from each other, the player and Bart have four bullets in their pistols. Turn-based game. On each turn of the game, the player has a choice: to go, shoot, hide behind the trough, run or surrender. [9]
- An independent group of computer users from Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) has developed a series of games from the DECUS software library - Digital Equipment Computer Users' Society (DECUS). DECUS members have created their own library of programs in BASIC. This library in 1970 included several computer games. These included: [9]
- "1queen" is a chess based game,
- "Apawam" - golf simulator,
- "Bandit" is a slot machine simulator.
1971-1980
1971
Main article: 1971 in computer games
Arcade machines
- In September, Bill Pitts created the first arcade game Galaxy Game based on PDP-11. In November, Nutting Associates released about 1,500 (of which 500 to 1,000 were sold) Computer Space arcade machines developed by Nolan Bushnell and Ted Dabney (see Ted Dabney on Wikipedia) (see also link and link 2). Thus, Computer Space is the first computer game published for the general public. Both games are variants of the implementation of the game Spacewar!
Games
- Don Rawich (Don Rawitsch) being a history teacher at Carleton College (Carleton College, Northfield, Minnesota, USA) was involved in creating educational software for HP 2100 microcomputers. In 1971, he had the idea to create not just a training program, but an educational computer game. To help implement such an unusual intention, he invited two friends Paul Dillenberger (Paul Dillenberger) and Bill Heinemann (Bill Heinemann). On December 3, 1971, a game called The Oregon Trail was ready and demonstrated to the public. The new tutorial turned out to be incredibly popular and turned out to be one of the most frequently performed programs of the educational institution, and also became widespread outside the college. The Oregon Trail is remarkable not only because it is one of the first educational computer games. The program became one of the most popular games in history, moving from the HP 2100 to Apple II computers, and then on the same platform in 1985 the first commercial version of the game was released. Later, new and new versions of games were released for various gaming platforms, including DOS, Macintosh, Windows, Nintendo Wii, Nintendo DS, Nintendo 3DS, Android, Windows Phone, iOS. For all the time managed to sell over 65 million commercial copies of the game [10] , which is an absolute record for training programs, as well as a very notable achievement, and in general in the industry of computer games. The Oregon Trail has become a rare and striking exception to the current rule of “learning games - sucks” [11] .
1972
Main article: 1972 in computer games
Companies
- At the beginning of the year, Syzygy was founded in the same year, renamed Atari.
Gaming consoles

Magnavox odyssey
- May 24 for the first time presented and demonstrated to the public Magnavox Odyssey - the first game console. The demonstration is attended by representatives of Nintendo and Atari. Nintendo later contracted Magnavox to release some of the Nintendo set-top boxes (so the first Nintendo game consoles were developed and produced by Magnavox, although selling Nintendo consoles on their own). Atari decides to develop a similar game independently, but in the form of an arcade machine. Since August 1972, Magnavox Odyssey has been on retail sale (US) at a price of $ 99.95.
Arcade machines
- On November 29, Atari releases the Pong arcade machine, developed under the impression of the Magnavox Odyssey demonstration. Pong became the first commercially successful arcade machine.
1973
Main article: 1973 in computer games
Companies
- March 19, 1973 Kajemasa Kozuki (Kagemasa Kozuki), together with partners, transforms his company into Konami Industry Co., Ltd., and at the same time the company announces a new direction of activity - the development of arcade machines.
Arcade machines
- In July, Atari launches its second arcade game Space Race - the first arcade game with joystick control.
Games
- In the walls of NASA, the Maze War game was developed - probably the first 3D first-person shooter game. The game was first implemented multiplayer game Deathmatch. In general, 1973 is considered the starting point for multiplayer shooters and 3D first-person shooters. This year there are several games that are still challenging the primacy in these genres - Maze War, Empire and Spasim.
- John Daleske wrote Empire - a computer game for the PLATO system. The game is probably the first implementation of a networked multiplayer shooter (or rather, the genre Shoot 'em up).
1974
Main article: 1974 in computer games
Companies
- Royal Philips Electronics acquires Magnavox and thus enters the gaming consoles market.
Arcade machines
- On November 5, 1974, Kee Games (founded in 1973 by Joe Keenan), broke into the Pong-market with a genius clone of Pong, which was called Tank. The gameplay of Tank was different from Pong. The players controlling the stains-tanks, had to get out of a complex maze, bypassing the minefields.
- Also in 1974, Atari released the first Gran Trak 10 racing game (gameplay and type of machine, article in the English Wikipedia).
Games
- March 1974 - Jim Bowery developed and released for the computer system PLATO a three-dimensional multiplayer computer game Spasim (short for "space simulation" (Russian space simulator )).
1975
Main article: 1975 in computer games
Companies
- Atari acquires Cyan Engineering, a developer of a Stella gaming system based on the recently released MOS Technology 6502 microprocessor.
Microprocessors

MOS Technology 6502
- In September, MOS Technology launches an eight-bit microprocessor 6502. With a performance similar to processors of other brands (primarily Intel and Motorola), it had more than seven times lower price, which explains its high popularity and lower prices for computers. The process of exiting computers from the “only for professionals and enthusiasts” category starts. The heart of the first home and gaming computers at affordable prices was often the MOS 6502. The prefixes of the first generation were implemented with a fixed logic circuit and, therefore, had one game (possibly in several variations). They did not contain a microprocessor, and therefore could not perform other algorithms. The release of second-generation consoles, which were based on a microprocessor capable of performing more complex algorithms, and therefore a large set of diverse and more complex computer games, was made possible by a sharp decline in prices for microprocessors, which was primarily due to the release of cheap and productive 6502 Up until the end of 1987, the 6502 (or its modifications) is the heart of the majority of gaming consoles sold. For a long time, until the end of the 90s, the processor 6502 (or its modifications) was often found in personal computers (including home and gaming), gaming consoles and arcade machines.
Gaming consoles

Pong
- Atari enters the gaming consoles market with the Pong model - initially through the Sears partner network under the Sears Tele-Games brand, and later through its own Atari Pong. Despite the fact that the console is an analogue of Magnavox Odyssey, it is waiting for an unexpected success. Many Pong-clones from other manufacturers appear on the market (it is significant that these consoles are often called Pong-clones, despite the fact that the similar Magnavox Odyssey game console went three years earlier). Some explain the success of the Atari Pong prefix by the fact that at the time of the prefix sales, for about three years there are very popular Pong slot machines with the exact same name, and many players were not averse to having a similar arcade machine at home, while about the same They did not even hear Magnavox Odyssey (given the fact that there was no arcade gaming machine called Odyssey).
Games
- Will Crowther (Eng.) Russian. creates the first version of the game Colossal Cave Adventure, the oldest known game of the genre quest.
1976
Main article: 1976 in computer games
Companies
- In October, Warner Communications buys Atari for $ 28 million and actually sponsors the continued development of the Stella project.
Microprocessors
Zilog Z80
- In July, sales of the Zilog Z80 microprocessor begin. Similarly, MOS Technology 6502, having high performance and low price, became one of the most common families of microprocessors and opened the way to affordable home computers and gaming systems. Along with 6502 it was often used as a part of home and gaming computers, arcade machines, game consoles and portable consoles. Interestingly, some products included both MOS 6502 and Zilog Z80, for example, the fairly popular Commodore 128 home computer. Some gaming systems, already released in the 2000s, such as the Nintendo Game Boy Advance, also contained part of the Zilog Z80.
Arcade machines
Breakout
- In April, Atari launches the new Breakout arcade machine - the development of the classic Pong. The game became the founder of the genre Breakout-arcades. The concept of the game was developed by Nolan Bushnell and Steve Bristow. The first technical implementation was performed by Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak. Despite the more complex algorithm, Breakout is still built on TTL elements and does not contain a microprocessor.
- Exidy releases the Death Race arcade. This is the first game to be widely condemned by the public for the high level of violence in the game, which caused mass protests and wide media coverage, which as a result led to the rapid completion of sales of this machine.
Gaming consoles

Fairchild channel f
- In November, Fairchild launches the Channel F game console (originally called Fairchild VES), the first second-generation game console. This is the first gaming console based on a microprocessor (Fairchild F8's own design) and running game programs recorded on cartridges. With the release of the Fairchild Channel F, the era of second-generation gaming consoles begins and the beginning of the sunset of the Pong-top boxes.
1977
Main article: 1977 in computer games
Computers

Apple II
- On July 5, Apple Computer launches an Apple II personal computer priced at $ 1,298. The Apple II (based on the MOS Technology 6502 microprocessor) is the first computer available as a ready-made device. The first graphic commercial games appear precisely for the Apple II computer. Despite the fact that by 1977 the PDP and PLATO systems already had a base of computer games, they were not accessible to ordinary people in terms of size or price, so familiarity with the first computer games for personal computers for most people began with Apple II computers. .
Arcade machines
- Cinematronics releases the Space Wars arcade machine. Space Wars is an arcade version of the 1962 Spacewar game! and claims to be the first widely accessible arcade machine with vector graphics and, accordingly, the first game with vector graphics available to the general public.
Gaming consoles
Indy 500 one of the games for the Atari 2600 available at the start of the console, demonstrates the typical graphics of games of those years

RCA Studio II

Atari 2600
- In January, Radio Corporation of America, following the Fairchild Channel F, releases its gaming console based on a microprocessor (developed by RCA 1802) RCA Studio II. This is the second console of the second generation. Like the Fairchild Channel F, the RCA Studio II is commercially unsuccessful - partly due to poor technical characteristics, partly due to the lack of a general understanding at the time of the type of computer games and, consequently, the lack of high-quality games that could be even more boring. Pong games.
- Nintendo re-enters the market for game consoles with the prefix Color TV Game 6. This time Nintendo produces consoles on its own (unlike in 1972, where consoles were completely developed and made by Magnavox). Nevertheless, most of the system components are made by a partner - Mitsubishi company. The prefix is another Pong-clone and at the time of release is already obsolete.
- October 14 (the announcement of the system was held on September 11, 1977) Atari releases the second-generation game console Atari 2600 (at launch it has the name Atari VCS). The Stella project - a gaming console based on the MOS 6502 microprocessor - turned out to be very expensive for Cyan Engineering, Atari and Warner Communications, but as a result, turned into the second-generation best-selling gaming console. Atari 2600 ported a large number of games from arcade machines and first released a large number of classic computer games. It is with the release of the Atari 2600 (and not the Fairchild Channel F) that many link the beginning of the era of the second-generation game consoles and the beginning of the platform boom. Atari 2600 seriously dominated the gaming consoles market - so for the entire era of the second-generation consoles, the Atari 2600 alone managed to sell much more than all the consoles of this generation of other manufacturers combined. [12] The Atari 2600 also proved to be the first commercially successful game console capable of launching games recorded on cartridges.
- At the end of the year comes another prefix of the second generation - Bally Astrocade. Due to production problems, the first sales took place only in 1978. The prefix can not be called successful, throughout the entire life cycle of the sale were very modest.
Games
- Walter Bright creates the Empire game (not to be confused with the 1973 Empire game for PLATO systems - see above ) for the PDP-10 computer - one of the first strategic games. Formally, the definition of a computer strategy game includes the computer implementation of a game of chess or card games, which by 1977 had already created a great many. Therefore, Empire officially cannot be considered the first strategic game. However, Empire’s merit is that it is not a computer implementation of an existing board or card game, but the first independent game with a more complex algorithm for the presenter (in this case, a computer). The game had a direct impact on the development of the genre of strategic games and possibly determined the features of future computer strategies.
- Mark Blank, Bruce Daniels, Tim Anderson and Dave Lebling create the first version of the Zork game for the PDP-10. Later, they founded Infocom and ported the Zork game to personal computers. Zork is the first commercial game of the text quest genre. At the same time, the game had a serious commercial success. Despite the small spread of computers in those days, the game Zork I sold 378,987 copies, which triggered the development of the Zork series, the development of the text quests genre, and a little later the text-graphic and graphic quests.
1978
Main article: 1978 in computer games
Companies
- The company Melbourne House was founded, which was originally engaged in publishing books, but already in 1980 the company mastered a new publishing business, publishing computer games for personal computers, and its own computer game production studio Beam Software was created as part of the company. [13] The company gained fame for the games The Hobbit (1982) (received the Golden Joystick Award in 1983), The Way of the Exploding Fist (1985) (won the Golden Joystick Award in 1985), Barbarian (1987) sequels of these games and other lesser-known projects.
Arcade machines

Space invaders
- In June, Taito launches the new Space Invaders arcade machine. The game becomes so popular that it causes a temporary shortage of coins of face value accepted by the machine. Space Invaders is the founder of the modern shoot-em up genre. Later the game was ported to almost all gaming platforms. After the release of Space Invaders for the Atari 2600, console sales increased 4 times. It is often claimed that the so-called “golden era of arcade machines” began with the Space Invaders game. [14] Space Invaders is the best arcade game of the Guinness Book of Records.
- Following Taito in the wake of the golden age of arcade machines, two more Japanese manufacturers Namco and Konami are entering the market. Both companies (in the future, leading providers of arcade entertainment) in 1978, released their first machines - Namco released Gee Bee, and Konami - Block Game.
Gaming consoles

Magnavox Odyssey²
- In July, Magnavox, as a division of Philips, is launching its second-generation Magnavox Odyssey² game console (in some countries, the console comes out under the names Philips Odyssey² and Philips Videopac G7000). Unlike other game consoles, Magnavox Odyssey 2 became an attempt to immediately enter two markets - a full keyboard on the case allows using the device not only as a game console, but also as a home computer. Magnavox Odyssey² was the first game console that was able to challenge the worthy challenge of the Atari 2600. The model was quite successful (by 1983, more than a million copies were sold), however, in terms of popularity, it could not be compared to the Atari 2600. Sales of the Atari console were several times higher. In fact, Atari annually sold about a million consoles a year, and in 1980, sales of the 2600th model reached a record high - about two million copies a year.
1979
Main article: 1979 in computer games
Computers

Atari 800XL is the most popular model from the Atari 8-bit computer series.
- In August, Atari launches the first 8-bit home computers, the Atari 400 and Atari 800 models. Subsequently, seven more models added to the lineup. Initially, the project was developed as a game console, which will replace the Atari 2600. But the unexpected success of Apple II computers forced Atari to rework the project and release a desktop computer instead of a game console. The Atari series of home computers based on MOS Technology 6502 was very popular, but Apple did not provide direct competition for computers. Apple II was a very common office computer, but with a price significantly lower than that of the Apple II, Atari computers more suited to the title of home computers. For the entire series, several thousand gaming programs were released, so Atari 8-bit computers became the first truly gaming home computers and had a great influence on the development and development of the commercial computer games market. Despite the high competition from the models of other manufacturers, computers of this series were produced before 1992.
Games
- Richard Garriot creates for Apple II the game Akalabeth: World of Doom - one of the first RPG games and the first game of the Ultima universe. To date, Ultima is one of the most popular fantasy game universes. Ultima games have come out and continue to go out on most popular gaming platforms.
- Richard Bartle and Roy Trabshaw create Multi-User Dungeon - a text-based multiplayer computer game with RPG elements. By the name of the game named a whole game genre - MUD. MUD games have been quite popular. For all the time it was released over a thousand different MUD games.
- For the Atari 2600 game console, the Adventure game is released by Warren Robinette. The game is the first implementation of the action-adventure genre. Later, the fame of the game brought the fact that Adventure is the first computer game in which the Easter egg was placed. In fact, the value of this “Easter egg” is quite large. Corporate policy Atari forbade placing in the games produced the names of the creators - all the games came with the signature "made by Atari". Taking into account the fact that the games, in addition to direct multi-million dollar profits, indirectly increased sales of the Atari 2600 consoles themselves, the game authors were unhappy that the company did not recognize the authorship of the real authors, and, accordingly, did not encourage the authors of many hits. In fact, the Easter egg Adventure is nothing more than the hidden name of the real author of the game. It was an internal conflict in Atari that provoked the emergence of many programmers from under the company's wing and the creation of several independent companies for the release of computer games, thereby breaking the monopoly of the creators of consoles to release games for them.
Arcade machines
Galaxian
- Using the success of Space Invaders, many clones of this arcade machine gun from other manufacturers come out, as Konami releases Space King, and Nintendo releases Space Fever and Radar Scope. By the way, the Radar Scope, released in Japan in December, became in 1980 the second most popular (after Pac Man) arcade machine in the land of the rising sun. Unlike most space shooters of the time, the game was made in a perspective projection emulating a three-dimensional environment. Inspired by the success of the game in November 1981, the North American division of Nintendo launches a large batch of arcade machines for sale in the United States and Canada. However, by this time the popularity of the Radar Scope in Japan had fallen dramatically, and in North America the machine did not arouse absolutely no interest. As a result, several thousand unsold arcade Radar Scope machines were copied at Nintendo's warehouses, which was undoubtedly a big financial blow for the company. Nevertheless, in 1981, Nintendo found use for this hardware ( see 1981 ).
- In the wake of the success of arcade machines, Atari launches its space-themed Lunar Lander (arcade simulator of the landing of the lunar module). The game did not enjoy great success, although later it was often released on home computers. However, continuing the theme of spaceflight in the same year, Atari launches another arcade machine gun, Asteroids. The game was a huge success and became the best-selling Atari game of all time. The popularity of the game was so high that the machines had to change the capacity to collect coins for more. The game was re-released on many gaming consoles of the eighties, while usually finding itself among the bestsellers for this console.
- Mentioning of space shooters can not be said about another representative of the classic games of the golden age of arcade games. In October, Namco launches the Galaxian arcade machine. Created as a competitor of Space Invaders, the game quickly gained popularity in many countries around the world. Later, Galaxian was re-released on many gaming platforms. The game had a great influence on the development of the genre Shoot 'em up. Developing the popularity of the game, several few-folds were later released - Galaga in 1981, the lesser-known Gaplus in 1984, as well as Galaga '88 (1987), Galaxian 3 (1990) and many less famous games of the series.
- Cinematronics launches the Warrior arcade machine, which is often called the first Fighting machine gun. Not very popular.
Companies
- On October 1, a group of four game developers leaves Atari, dissatisfied with the company's internal policy, and founds its Activision company. The company became the first independent developer of computer games for gaming consoles and home computers - before that, the development of games for gaming consoles was done only by manufacturers of these consoles. Today, Activision is the largest gaming company in the world. The annual turnover is about 5 billion US dollars. Activision quickly begins to produce new high-quality games for the Atari 2600, which on the one hand increases the popularity of the console, but on the other does not bring direct profits to Atari and even creates competition for games released by Atari. This situation does not suit Atari (especially when you consider that the company was created by former Atari employees, as well as in Activision, the outflow of personnel continues). As a result, Atari sues Activision in court, in order to oblige to pay part of the profits from the sales of games for the Atari 2600 in favor of Atari, but the court decides the case in favor of Activision, and following the example of Activision, many new game developers for Atari 2600 appear, and then other home gaming systems.
- Founded the company Sierra Entertainment (originally called On-Line Systems, in 1982 was renamed Sierra On-Line). The company's goal was to develop graphics games for the Apple II computer, but the company became famous for many original games for other platforms. The company is known primarily as the creator of the first graphic quest Mystery House, and is the founder of the genre. Moreover, the company has long been considered the creator of the best graphic quests. This company created such famous series of quests as King's Quest, Space Quest, Leisure Suit Larry, Police Quest. The company also acted as a publisher of games from third-party studios.
Portable game consoles

Milton Bradley Microvision
- In November, Milton Bradley launches the first portable gaming console with interchangeable Microvision cartridges. Despite the imperfection and unreliability of the system (the number of failures was very large), as well as the poor performance of the console and very primitive graphics (a monochrome screen with a resolution of 16x16 pixels with a fairly high latency when changing the image) was quite popular. Microvision was on sale only three years, but during this time more than eight million devices were sold.
1980
Main article: 1980 in computer games
Companies
- The first companies producing computer games for 8-bit home computers appear. One of these companies is Bug-Byte Software Ltd., which was engaged in porting games from arcade machines to home computers, but was also involved in the development of original games. The most famous company brought a platform Manic Miner (1983).
Computers

Sinclair ZX80

Acorn atom
The year 1980 was the starting point for truly affordable home computers. Sinclair Research releases the ZX80, the first computer in the UK for less than £ 100. The device was available as a kit for assembly at a price of 79.95 pounds or as a finished device at a price of 99.95 pounds. Virtually any British family that had the desire to buy a home computer could afford it. The computer was quite popular (over 100 thousand devices were sold) and at first had no competitors in the busy price range. The main competitor of the ZX80 was Acorn Computers' Atom computer, which came out in the same year at a price of 120 pounds as a set for assembly, 170 pounds as a complete device, and more than 200 pounds for the older model. After a short time, home computers from other manufacturers began to appear on the market at an affordable price, but since 1980 and with the Sinclair ZX80, many people connect the beginning of the home computer era. Computer Sinclair ZX80 was built on the base of the microprocessor Zilog Z80, and Acorn Atom —MOS Technology 6502.
Arcade machines

Pac-man
- On May 22, Namco launches an arcade machine game with a game developed by Tor-Ivatani Pac-Man [15] (originally produced under the name PUCK MAN, but at the start in the United States was renamed Pac-Man). Pac-Man is one of the most popular video games, and the image of Pac-Man heroes is one of the most recognizable. Pac-Man was the first super-popular video game that was neither a space shooter nor a Pong system. In fact, the game had a serious impact on the development of all genres of arcade games, as it demonstrated the gameplay, which is not a shooter, the style of the game did not involve violence and was interesting for wider segments of the population than space shooters. Changing the genre has pushed other video game developers to create other non-standard arcade games. Many arcade games have been developed as an attempt to create a similar extra-genre game. Among the games that were created under this influence appear many classic arcade games - Q * bert, Donkey Kong, Frogger and many others. Subsequently, the Pac-man game was ported to almost all gaming systems.
- In the arcade segment, Atari launches the Missile Command game. The game touches the topic of the Cold War at the time, making it one of the most popular arcade entertainment of the year. Missile Command was later ported to most gaming systems, and also often referred to as one of the most visible phenomena of the golden age of arcade video games.
- Data East company produces the world's first unified arcade machine DECO Cassette System. Unlike other arcade machines that used unique equipment for each new game, the DECO Cassette System was an arcade machine for which a variety of game programs were produced on removable media. The games for the machine were released on ordinary audio compact cassettes and electronic keys as copy protection. Despite the fact that the idea of a single hardware architecture for several games did not become popular at that time, nevertheless, over time, almost all manufacturers of arcade machines released their models of universal arcade systems. At the same time, over the entire period of production of the machine, over 35,000 pieces of the DECO Cassette System were sold, and it was on this arcade platform that many classic arcade hits appeared, including: BurgerTime, Bump 'n' Jump, Boulder Dash, Nebula and many others.
- The company Atari in November 1980, released an arcade machine Battlezone. Thanks to the novelty of the gameplay and graphics, the game has been popular for a long time.
Gaming consoles

Mattel intellivision
- Mattel releases its version of the second-generation game console Intellivision (trial sales took place back in 1979, but massive sales began only in 1980). Although the prefix did not reach the popularity of the Atari 2600, it was nevertheless quite successful - over the entire period of availability of the console from 1980 to 1983, more than three million devices were sold. Mattel Intellivision is the first game console built on a 16-bit microprocessor (General Instrument CP1600). In addition, it is worth noting the game controller Intellivision. It was his appearance that was decisive for the majority of subsequent game consoles of the second generation. Intellivision-shaped controllers together with Atari joysticks remained the main means of computer games control until the release of gamepads with the third generation of game consoles.
- In the market of game consoles an interesting situation. After three years since the release of the Atari 2600, several technically more advanced game consoles appear on the market (first of all, Magnavox Odyssey² and Mattel Intellivision). But, in 1980, Atari released several games for the Atari 2600 - ports of popular arcade games such as Space Invaders (the original arcade game Taito) and Asteroids (the original arcade of the Atari itself). As a result, sales of the console do not decrease, but, on the contrary, double and reach a record level - 2 million consoles per year.
Portable game consoles

Nintendo Game & Watch
- April 28, Nintendo launches the first device in the Nintendo Game & Watch series. Game & Watch is a series of handheld handheld gaming devices based on a special segmented LCD. One device allowed to play only one game. The devices were very popular and were produced from 1980 to 1991. During this time, more than 43 million devices have been sold. The release of Game & Watch was the first big success for Nintendo. The popularity of these gaming devices led to the emergence of other versions of devices from other manufacturers, as well as clones of devices all over the world (including from 1984 and in the USSR under the “Electronics” brand). In addition, Nintendo Game & Watch can be called the first successful portable game console.
Games

Mystery house
- Michael Toy , Glenn Wichman and Ken Arnold create a full-screen RPG for UNIX systems — Rogue, which spawned a whole subgenre known as Roguelike (Rogue-like games). The subgenre itself had a serious impact on the development of the entire RPG genre. Over the entire existence of the subgenre, a huge number of Roguelike games have come out (and continue to go out)
- Doug Carlston creates the Galactic Empire game for the TRS-80 computer. His brother Gary ( Gary Carlston ) is setting up the sale of the game. The business is so good that the brothers set up a company for the production and distribution of video games Brøderbund, which will later give the world a lot of games that eventually became classics.
- On-Line Systems (Sierra Entertaiment) releases the first graphic adventure game Mystery House for the Apple II computer. Control of the character is still carried out by entering text, but what is happening in the game is now displayed in the form of static black and white vector drawings, which was undoubtedly a breakthrough in the genre of adventure games. This game is called the founder of the genre of graphic quests. Mystery House was very popular and sold 15,000 copies (a major achievement for a computer game of those times).
1981–1990
1981

Ms. Pac-man

IBM 5150

Sinclair ZX81
Donkey kong

BBC Micro
Atari tempest

Commodore VIC-20
Kaboom! one of the popular games for the Atari 2600

3D Monster Maze
Main article: 1981 in computer games
On January 13, Midway Games, which sold the original Pac-Man game in the USA, released the sequel to the series - the Ms. game. Pac-Man. According to some estimates, the game has surpassed the original in popularity. So given the fact that the machine was sold mainly in the United States, however, the arcade ranks fifth in sales in the world. Some reputable publications believe that Ms. Pac-Man simply “eclipsed the original Pac-Man” [16] . The game was reprinted for almost all popular gaming home systems and occupies one of the leading places in the golden age of arcade video games and is a recognized classic of arcade video games.
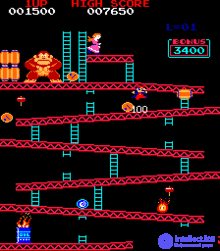
July 9, Nintendo launches arcade game Donkey Kong. The game is one of the first implementations of the platformer genre and is one of the classic arcades of the golden age of arcade video games. Donkey Kong is one of the three most popular arcade machines in the world. Like many popular arcade games of the time, Donkey Kong was ported to many home gaming systems. Interestingly, the original game Donkey Kong was created in order to find the use of unsold machines with the game Radar Scope. In the warehouses of Nintendo, several thousand arcade machines of the Radar Scope accumulated, and it was decided to develop a new game for the existing hardware platform. The fact that the game will be a hit and will take place in the top three best-selling arcade machines of all time, no one imagined. Moreover, the game became the first game in the Donkey Kong game series, one of the most popular game series of modern times. As of the end of 2011, about 54 million games have been sold in the Donkey Kong series. It is worth noting that the game first appeared the popular video game character Dank Kong. Also, the game character Mario first appeared in the game (so far under the name of Jumpman), and thus Donkey Kong is the first game of the Mario series of games - the most popular franchise in the world ( as of 2012, more than 460 million copies of the series were sold ) .
In July, another classic arcade game is released: Konami releases the game Frogger. Arcade is fast becoming popular all over the world. Like many classic arcade games, the game is released on most home gaming systems. It is interesting that the Frogger arcade machine technically is one of the first multiprocessor arcade machines - the heart of the machine (or rather the hearts) of the machine was two Zilog Z80 processors.
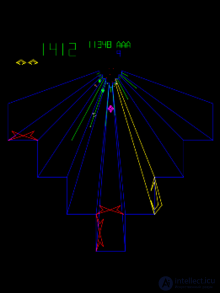
Atari launches new Tempest space shooter. The game was conceived as a 3D version of the classic Space Invaders, but technologically at the time this idea could not be realized. The creators had to develop a new gameplay, resulting in the birth of a new subgenre of shooters, now known as tunnel shooters. Игра пользовалась большой популярностью. Во всем мире было установлено более 29 тысяч игровых автоматов с этой игрой. Tempest признана классикой золотого века аркадных видеоигр. Согласно наблюдений некоторых изданий, игра входит в десятку самых популярных игровых автоматов в мире [17] . Ещё игра выделяется тем, что впервые использует технологию цветного векторного дисплея Atari QuadraScan и, таким образом, является первой массовой игрой с цветной векторной графикой.
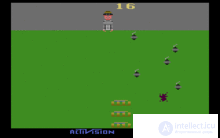
Atari, adopting the previously tested successful tactics to produce the best arcade games on the Atari 2600, releases the Ms. Pac-Man and Centipede. Both games quickly become bestsellers, which only increases the popularity of Atari gaming console. However, not only the ports of the arcades become bestsellers. So, at that time, the young Activision company released several original games in 1981, which are also becoming very popular. Among them it is worth mentioning separately the game Kaboom !. The game is in the top ten best-selling games for the Atari 2600 and has been reprinted for many other gaming platforms. The game received high marks from most reputable publications, and won the popularity of players for the simplicity and originality of the gameplay.
Do not think that for other platforms does not go the original and interesting games. So it is worth mentioning the Utopia game released in 1981 for Mattel Intellivision. The game has become very popular for its original gameplay. In fact, Utopia is one of the first graphic simulators of urban planning and urban management. The game had an impact on the development of turn-based strategy genres and simulators of city management.
In the sector of game consoles lull. In 1981, there is not a single second-generation new console, except for trial sales of the SEGA Game 1000 (also known as SG-1000). This model is the first attempt of SEGA to enter the market of game consoles, but, after trial sales, SEGA postpones the exit of the console until 1983.
A significant event takes place in the world of computer games - Muse Software launches the Castle Wolfenstein game for Apple II computers - the first stealth action game. The game became quite popular and was released for other popular desktop computers (IBM PC, Atari (8-bit series), Commodore 64). The game had a great influence on the development of the stealth action genre and many action games.
There are new manufacturers of games for home computers. The company is based Mikro-Gen known as the creator of the famous games Pajamarama, Everyone's A Wally, Three Weeks in Paradise, Equinox and other games. In the same year, Hewson Consultants was established, which established itself as the creator of quality games for home computers. The company has released many games, many of which have become bestsellers and have been awarded numerous awards, for example: the Uridium and Cybernoid series of games, Paradroid, Nebulus, Cybernoid and Exolon games. Finally, in the same year, Quicksilva was founded, releasing the famous Ant Attack and Zombie Zombie games. It is worth mentioning the company Softdisk based in the city of Shreveport in 1981. The company is now famous for the fact that it is within its walls that a group of computer game developers known as Id software has gathered. Nevertheless, such famous game series as Rescue Rover, Dangerous Dave, Catacomb (including the famous Catacomb 3-D and Catacomb Abyss), as well as the games Shadow Knights, Commander Keen: Keen Dreams and Hovertank 3D were created or published in Softdisk.
The “invasion” of home computers that began in 1980 continued with a new force in 1981. Developing its success in a new market for itself, Sinclair Research releases the Sinclair ZX81, an improved and even cheaper model of a home computer. Despite the increased characteristics of a home computer, its price in the form of a kit for assembly was only 49.99 British pounds, and in the form of a finished assembled product - 69.99 pounds. Sinclair ZX81 became the first desktop computer worth less than 50 pounds. The success of this model was even more significant than the success of its predecessor - in just a year, nearly 400,000 copies were sold. Significant competition in the British market for Sir Clive Sinclair’s computers was once again only Acorn Computers.
Acorn was just finishing a new model called Proton, which was to replace the Acorn Atom. At this time, the British Corporation BBC (British Broadcasting Corporation) is launching a project to create a national desktop computer. The future Acorn Proton fits the BBC specification and soon saw the light called BBC Microcomputer (or later better known as BBC Micro). The Acorn computer was significantly more expensive than the ZX81 - 299 pounds and 399 pounds depending on the model, so this popularity, which had the ZX81, in 1981 did not have, however, had a permanent advertisement on national television and a long enough period of sales, to 1994 BBC Micro overcomes the mark of 1.5 million copies sold.
In the United States, against the backdrop of the high popularity of Apple II computers and the highly successful line of 8-bit Atari home computers, Commodore Business Machines has released its version of cheap home computers - the Commodore VIC-20 model. Appearing at a price of 299.95 US dollars and sold for 4 years, VIC-20 found its fans all over the world and sold 2.5 million copies.
Each of these computers has found its own army of users and, of course, a large library of application programs, and, of course, computer games. For these computers there are several thousand computer games, some of which are very original. For example, the 1981 game for Sinclair ZX81 called 3D Monster Maze (sponsored by Malcolm Evans) becomes the first three-person first-person game for a personal computer.
Also this year there was another significant event in the personal computers sector. On August 12, IBM released its first mass personal computer under the modest name of the IBM 5150 model, or better known as the IBM PC. And although at the time of release, the model did not even have a graphics mode, it turned out to be very popular, and the architecture of the IBM PC for a long time became dominant in the PC market. Today, it is IBM PC-compatible computer that is the most common architecture in the personal computer market, and the PC platform is the most popular gaming platform in the world. And the IBM 5150 model is the ancestor of the modern PC platform.
1982
Main article: 1982 in computer games
By 1982, the number of gaming systems sold (home computers and gaming consoles) reached a critical number, and computer entertainment dramatically changed many areas of society. A lot of new video game periodicals are coming out. Following the BBC (see above), programs about computers and computer entertainment appear on other channels - one of the most popular shows of the time is the gaming TV show, which appeared in 1982, Starcade (channel WTBS, USA). Animated series appear, the main characters of which are the heroes of video games. There is also a counter-situation - this year a huge number of video games based on comics, animated series and popular films are released. Following Activision in the market, there are many new companies producing video games. Many large entertainment companies enter the gaming market. The games themselves are becoming more technological - some genres are finally formed (primarily auto simulators, shooters and platformers), and new technologies are actively used - such as isometric projection, Parallax scrolling ( English ), games using undocumented features of the gaming platform appear. All sectors of the video game market are actively developing: in 1982, many new arcade machines, new home computers, computer games, game consoles, handheld gaming devices and video games for game consoles were released. The most popular home gaming system remains the Atari 2600, but this year the game console and its creator become the center of events negatively reflected in the entire game console industry.
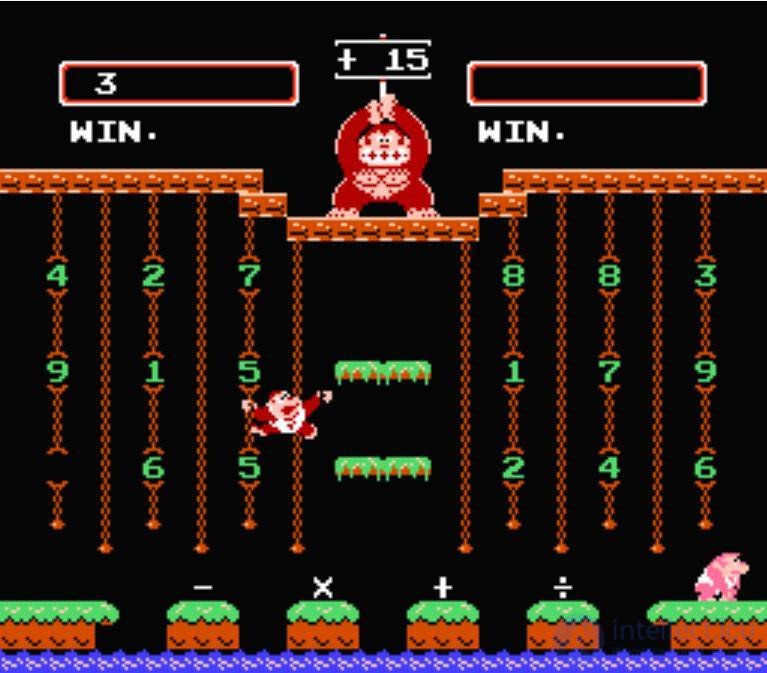

Donkey Kong Jr.
In the wake of the success of the arcade machine Donkey Kong, in August, Nintendo launches a new arcade machine Donkey Kong Jr. The game is another early implementation of the arcade platformer. And although the “junior” could not repeat the success of the original, it nevertheless firmly took place in the list of classic games of the golden age of arcade machines and is among the ten most popular slot machines in the world. Like many popular games, later Donkey Kong Jr. was re-released for most home gaming systems, thereby only increasing its popularity. Interesting is the fact that the game is the only one where Mario plays the role of the supreme villain.

Q * bert
Despite the fact that Donkey Kong Jr. became the most popular arcade machine of 1982, the game had to experience a huge competition. In the same year a large
продолжение следует...
Продолжение:
Часть 1 The history of computer games
Часть 2 1983 - The history of computer games
Часть 3 1984 - The history of computer games
Часть 4 - The history of computer games
Часть 5 1991—2000 - The history of computer games

































Comments
To leave a comment
Computer games developming
Terms: Computer games developming