Tester-like profession
Error Catcher, Program Taster
The profession of a tester (QA-specialist) is becoming increasingly popular in the computer industry. Companies in a highly competitive environment seek to provide the consumer with the highest quality product. QA specialists are often novice programmers with a passion for computer technology who are ready to check codes and calculate errors, keep abreast of IT developments.
general description
A tester is a specialist who evaluates software quality. It performs two functions: user and software expert. The abbreviation QA stands for quality assurance, which literally means “quality guarantee” in English. “Despite the fact that it is rather difficult to touch the fruit of a QA-specialist’s work, it directly affects not only quality, but also the very essence, the product concept,” says Alexander Zaliznyak, GlobalLogic tester. Testers look for bugs and software malfunctions, and then give programmers feedback. Thus, the tester or testing group becomes indispensable in the process of software release - a kind of filters for product flaws before entering the market. Often, QA-specialists become not due to skills and vocation, but for the sake of sports interest: such people are attracted by the opportunity to be the “pioneer” of a new program or computer game. There are also alpha and beta testers. The former, together with the programmers, work on the product and are engaged in full or partial testing. A beta tester is a user who performs the functions of beta testing, as well as officially published versions, and so on. release candidates of the program.
Education
Ukrainian universities do not offer specialized education for testers. There is an opinion that a QA specialist is a failed programmer. In fact, it is not. However, it is not really necessary to be a programming genius to test software. As a rule, employers welcome higher technical education in the field of information technology (for example, in the following specialties: “automated information processing systems and management”, “computers, complexes, systems and networks”, “computer science and computing equipment”, “information systems and technology"). A good addition to the tester's resume is a certificate of completion of specialized courses, especially on automated testing, as well as the availability of international ISTQB Certified Tester Foundation Level.
Functional responsibilities
The main functionality of a QA-specialist can be formulated as follows:
Development of plans, schedules, methods and descriptions of testing.
Artificial creation of situations that in actual use of the program may give an error.
Development of test software modules.
Filling database tables with test indicators.
Feedback on the analysis of the results obtained during the passage of the tests.
Control of the process of eliminating the detected errors by the software developer.
Communication with developers and clients.
Knowledge, skills
Obviously, the tester should be well versed in the Internet, have the skills and experience with web applications. Employers welcome knowledge of HTML, JavaScript. Prefer candidates with experience of two years in the development and testing of software, test documentation. An advantage in employment will be the availability of experience with Oracle and / or MS SQL DBMS, as well as the use of test automation tools. Frequent desire of companies is the availability of knowledge and experience in the field for which software is developed (for example, when working with the 1C program - basic knowledge in accounting). If the work involves communication with foreign clients, fluency in English is required.
Personal qualities
The work of the tester is painstaking, and therefore requires attentiveness, patience and perseverance, a willingness to work on improving the program from version to version. The tester must have excellent memory and analytical thinking, be balanced and reasonable. QA-specialist helps communication skills and ability to work in a team. Readiness to strictly follow the rules is appreciated, but at the same time initiative and curiosity, interest in experiments is welcomed. A tester is, in fact, an engineer and a user in one person, so he should be able to analyze the product from the standpoint of both.
Pros and cons of the profession
An undeniable positive feature is the ability to work remotely. It is also worth noting that today the demand for testers exceeds supply in the labor market, and therefore they will not remain without work. In addition, this position is a good basis for professional and career growth. This is confirmed by Alexander Zaliznyak: “Ukrainian testers often have to work with foreign customers, thanks to which their knowledge of the language, understanding of cultural differences and business ethics are improved. And this is useful not only for testers, but also for every professional. ” The disadvantages include the monotony of the working day. But this argument does not seem so compelling, given the prospects for upgrading to more responsible and creative IT positions and the possibility of changing the project, a chance to be the first to see and "taste" the new program. Sometimes the work of a QA-specialist is complicated by the fact that the company does not have the necessary basic resources - for example, documentation of software errors, which requires re-testing and negatively affects the results of work. But this is rather the problem of individual employers, rather than the profession as a whole.
Salary
The salary depends on the complexity of the project the tester is working on and his level of responsibility. On average, Ukrainian companies offer a reward of 2.5 to 12 thousand UAH.
Perspectives
QA-specialists have the opportunity for vertical career growth. For example, they can reach the following career heights: lead tester or test team leader. That is, from a simple executor to grow up to a manager, and this requires a qualitatively new set of knowledge and skills - from the basics of psychology to the art of managing a company. In addition, a tester is an excellent preparation for a programmer's position: analyzing and evaluating software, a QA-specialist can create it in the future. The perspectives of the tester depend on the specifics of the work - he can become a test designer or test analyst, and then an automated testing engineer. It is quite possible and horizontal professional development - through the development of new testing technologies, participation in projects with different content.
IT specialists are trained in 7 major bachelor degrees:
- Computer science,
- System engineering,
- Software engineering
- Computer engineering,
- Applied Mathematics,
- Security of information and communication systems,
- System analysis.
"Computer science"
Graduates will learn to perform and create:
- conduct a systematic analysis of subject areas
- create mathematical models of objects and automation processes,
- design and develop application software and databases
- apply software development tools, web technologies, distributed systems technologies and parallel computing,
- develop artificial intelligence systems.
- software and hardware computer systems and networks, databases, information security tools,
- expert systems
- semantic web and grid networks
- parallel processing methods
- data virtualization methods.
"Computer engineering"
Graduates will learn to develop:
- hardware and software of IT, computer systems and networks,
- their system software and databases
- technical means of information protection,
- decision making systems
- diagnostic and testing systems
- distributed and cluster computer systems,
- local, global and corporate computer networks.
The main difference between “computer engineering” and “computer science” is that “engineering” deals with internal problems in relation to a computer (that is, how computers and computer systems work and work). "Sciences" deal with the problems of using computers to create IT and / or solving problems in various subject areas.
"Software Engineering"
Graduates will learn to create application software:
- computer systems and networks
- corporate systems and networks
- decision support systems
- automated control systems
- intelligent systems
- multimedia systems
- business software
- web portals
- databases and knowledge
- software diagnostics and certification systems,
- software protection of information in computer systems and networks
and:
- manage content, timing, cost and quality, human resources, risks in software development,
- use languages of the description of architecture and interface, patterns, notations, strategies,
- test software at the modular, integration and system levels, focused on formal specifications, data flows, conditions of use, determination of reliability, performance,
- develop design working technical documentation.
"System Engineering"
Graduates will learn to create:
- computerized and robotic systems,
- automation systems designed to control technological processes, technical objects and business systems built on the basis of the ICS,
- means of protecting information and databases and knowledge,
- management theory and decision making
- The latest programming technology and artificial intelligence.
"Applied Mathematics"
Graduates will learn to create:
- models of processes and phenomena
- mathematical and software information processing systems,
- artificial intelligence systems
- algorithms for solving problems and planning computational experiments,
- expert systems.
- automated data processing systems
- models and technologies for cryptographic protection of information, authentication, digital signature, cryptographic protocols,
- cryptographic tools in banking, commercial and other areas.
"Security of Information and Communication Systems"
Graduates will learn to create:
- information security and security policies in computer systems and networks,
- protection of verbal information and information in telecommunication networks and communication systems,
- complex information security systems based on software and hardware and software information security tools,
- software and technical methods of information protection,
- cyber security support systems.
"System Analysis"
Graduates will learn:
- conduct a comprehensive analysis
- use decision-making technologies in complex systems of different nature,
- use modern information technologies and computer equipment for building and maintaining information computerized systems in various fields of science and national economy,
- using mathematical methods and software (C, C ++, Java, databases) to solve problems in various fields of science, technology, finance, socio-economic and political spheres.
Summary
| Direction of training |
|---|
| Computer science is prepared by modern IT specialists with comprehensive knowledge of software and hardware, who clearly understand the interaction of application programs and computer systems and have skills in four main areas: algorithmic thinking, information presentation, programming and system design. |
| System engineering is designed to provide training for specialists in the development and implementation of computerized management information systems. Systems engineering covers the processes of describing, designing, implementing, testing, implementing and maintaining complex systems as a whole. |
| Software engineering teaches the construction of complex software systems that require the coordinated work of teams of programmers of different specializations and qualifications. This direction, in addition to programming itself, is intended to teach a systematic process of designing, developing and maintaining software. |
| Computer engineering is engaged in the development of computer systems and networks nodes and their integration, research in the field of robotics. Computer engineers design individual microprocessors and computers, integrate them into systems and networks. Their tasks include writing software for embedded microcontrollers, designing VLSI (extra large integration scheme), developing operating systems, designing analog sensors, etc. |
| Applied mathematics provides training in the fields of application of mathematical methods to scientific, technical and production problems. As a tool, specialists use IT tools to solve a wide range of engineering problems in industrial, economic, environmental, economic, and cybernetic activities. |
| Security of information and communication systems is prepared by specialists capable of developing and using mathematical methods, models, software and hardware and software for protecting information in the SEC (developing models of threats and violators, risk analysis, shaping security policies, software for protecting information, cyber security). |
| Systems analysis teaches you to make decisions based on mathematical research methods. System analysis is a set of methods based on the use of computer technologies and focused on the study of complex systems - technical, economic, environmental, etc. The result of system research is the choice of a well-defined alternative: a regional development plan, design parameters. |
QA / QC / Test Engineer
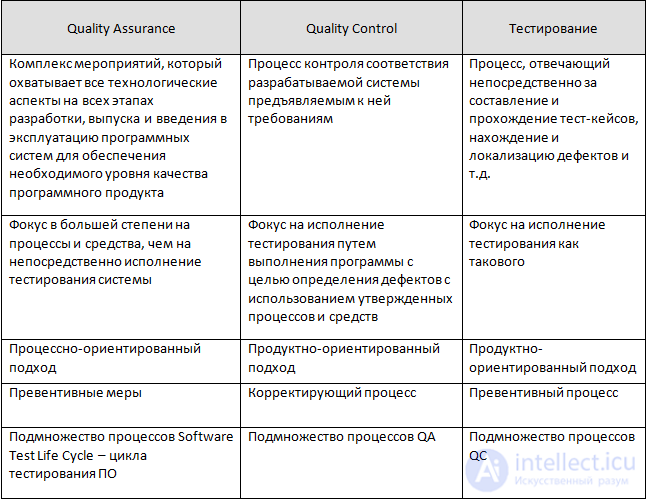
Thus, we can build a model of the hierarchy of quality assurance processes: Testing is part of QC. QC is part of QA.


Comments
To leave a comment
Quality Assurance
Terms: Quality Assurance