Lecture
Scheme 11.1. Social management levels
Chapter 11, Social Management ____________________________________ 141
Social management is a public activity of people to coordinate the work of individuals, social groups, organizations, society as a whole.
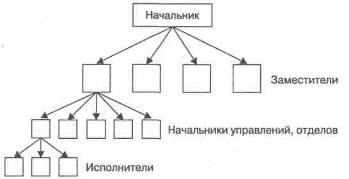
As society grows and differentiates, it is becoming increasingly difficult to manage it unprofessionally. Hence, the need for separation of managerial activity is clear. The larger the organization, the greater the amount of managerial work that needs to be done to achieve your goals. It follows that the leaders themselves must be structured, and such structuring will have both horizontal (arrangement of heads of related units) and vertical character (arrangement of leaders by levels) (Figure 11.1).
Scheme 11.2. Leveling leaders
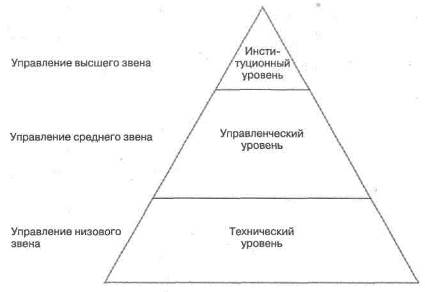
The vertical allocation of the level of managerial activity is called the level of management. Regardless of management levels, managers are traditionally divided into three categories. T. Parsons examined these categories of managers in terms of the functions they perform in the organization:
• at the technical level, people are engaged in daily operations necessary to ensure efficient work without disruption;
• at the managerial level, managers are involved in the coordination and direction of the activities of individual links within the organization;
• at the institutional level, managers develop long-term plans, formulate goals, adapt the organization's activities to the external environment (nature and society) (Figure 11.2).
In addition, all management personnel are divided as follows.
Top managers. These are operational, primary managers, direct managers of workers, executors (master, department head, department head, department commander). This is a large part of the leaders. A characteristic feature of their work is tension and a frequent change of action. The implementation period is short, usually about two weeks. The focus of their activities is on subordinates; to a lesser extent - to communicate with peers, even less so - with a superior.
Middle managers. They coordinate and oversee the work of grassroots managers. Recently, in all organizations the role of this link has increased significantly; the number of middle managers also increased. In some organizations, middle managers are divided into:
• upper mid-level;
• lower middle level.
Comments
To leave a comment
Sociology
Terms: Sociology