Lecture
 A production model or a model based on rules allows you to represent knowledge in the form of sentences (products) such as: “If (condition), then (action)”.
A production model or a model based on rules allows you to represent knowledge in the form of sentences (products) such as: “If (condition), then (action)”.
A condition is understood as a certain sample proposal, which is searched in the knowledge base, and under action - actions that are performed when the search results are successful (they can be intermediate, which then act as conditions, and terminal or target, terminating the system).
When using the production model, the knowledge base consists of a set of rules. The program that controls the rules is called an output machine. Most often, the output of the result is direct (from data to search for a target) or the opposite (from the goal to confirm it - to the data). The data are the output facts from which the output engine runs.
If a certain set of products is stored in the system's memory, then they form a production system. In the production system, special procedures of product quality management should be set, with the help of which the products are updated and the execution of a particular product is updated.
The production system contains a database of rules (products), a global database and a management system.


Expert medical systems are designed to provide prompt and systematic assistance to medical personnel in solving problem situations and making decisions on patient treatment issues. Expert systems are built on the basis of laws, regulations, national recommendations and rules adopted in a medical institution. The functionality of such systems consists of the following major integrated components: a module for collecting and storing expert data and a module for generating the necessary expert solutions.
The tasks of the medical expert system are:
Diagnostic tests are anonymous and free. After the survey, a report is generated indicating the probabilities of possible diseases. The report can be printed or received by mail.
 http://homeopath-expert.com/ru
http://homeopath-expert.com/ru
Here you can find a homeopathic remedy with high accuracy based on the symptoms. In order for this expert system to give the correct result, you need to enter the symptoms in the field to quickly search OR use the questionnaire, marking the corresponding symptoms with a check mark. You must select at least four symptoms.
 http://www.diagnos.ru/
http://www.diagnos.ru/
The diagnostic system Diagnos.ru is the only interactive telemedicine diagnostic system, as well as the largest in the world in the number of groups of diagnosed diseases and patient categories. Currently, more than 240 diseases and more than 600 nosological units are diagnosed. A nosological unit is a specific disease that is isolated as an independent disease, usually based on established causes, developmental mechanisms, and characteristic clinical manifestations.
The diagnostic system consists of two parts (programs). The first analyzes medical data using a number of modern mathematical methods. The second - the one that is located directly on the website Diagnosis.ru - collects information about the patient and issues a diagnosis based on the ready-made correspondences created by the analyzer.
Technically, the diagnostic system is an artificial intelligence based on fuzzy logic. Answers to questions that the user gives come in a clear form. On the basis of certain combinations of answers, fuzzy assumptions are formed for syndromes and diseases in which the system may be strengthened or disappointed. Depending on those or other assumptions, the user is asked new questions. At the end, a presumptive diagnosis is issued.
Another principle of the system - the complexity of the conditions for diagnosis. For example, having only one abdominal pain will never give even a minimal likelihood of a disease. But the combination of even slightly pronounced symptoms can significantly increase the likelihood of an appropriate diagnosis. The diagnostic system gives the percentage probability of diseases, and not just an assumption about their presence or absence.
Due to the fact that the diagnosis covers all systems of human organs, it became possible to diagnose systemic diseases with complex multiorgan lesions. What does the diagnostic system give to patients and doctors? For a patient, this is a list of possible diseases with an indication of probability, recommendations for visiting specialists and comments on the current state. For doctors - the opportunity to see the history and immediately without any additional questions to have a conclusion.
 The semantic network is an information model of the domain, has the form of a directed graph, the vertices of which correspond to the objects of the domain, and the arcs (edges) define the relations between them. Objects can be concepts, events, properties, or processes.
The semantic network is an information model of the domain, has the form of a directed graph, the vertices of which correspond to the objects of the domain, and the arcs (edges) define the relations between them. Objects can be concepts, events, properties, or processes.
Thus, the semantic network is one of the ways to represent knowledge. The title combines terms from two sciences: semantics in linguistics studies the meaning of language units, and the grid in mathematics is a kind of graph — a set of vertices connected by arcs (edges) to which a certain number is assigned. In the semantic grid, the concept of a knowledge base plays the role of vertices, and arcs (as a rule, are directed) define the relations between them. Thus, the semantic network reflects the semantics of the domain in the form of concepts and relationships.
http://wordnetweb.princeton.edu/perl/webwn
WordNet is a semantic web for English developed at Princeton University and released with free software accompanying software.

The basic vocabulary unit in WordNet is not a single word, but a so-called synonymous series (“synsets”), which combines words with a similar meaning, connected by synonymy relations, that is, the division of the set of all lexical units into equivalence classes expressing the essence or concepts.
Examples of synset {good, fine}, {man, adult male}.
WordNet is a semantic network, in the nodes of which there are synsets associated with various relationships, such as Hyponyms, Hyperonyms, Golon, Meron, and the like. Each synset has a description in natural language and examples of the use of words in context.
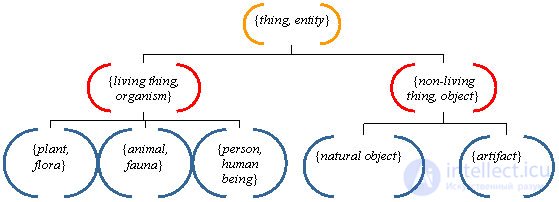
The dictionary consists of 4 networks for the main parts of speech: nouns, verbs, adjectives and adverbs. A word or phrase may appear in more than one SINC and have more than one category of a part of speech. Each synset contains a list of synonyms or synonymous phrases and pointers describing the relationship between it and other syncetams. Words that have several meanings are included in several synsetes and can be assigned to different syntactic and lexical classes.
| Hypernym | generalization | Animals are hypersensible dogs |
|---|---|---|
| Hyponym | detailing | The dog is an animal hyponym |
| Meronym | part from | Doors are the Meronim of the house |
| Holonym | contains components | The house is holonyma doors |
| Synonym | similar meaning | Car is synonymous with car |
| Antonym | opposite meaning | Like is antonym not like |
| Entailment | necessary action | Step is an unfoldable moves |
Also, there are various other links: lexical, antonyms, contextual (the word "X" refers to the word "Y") and others. Hyponymia plays a special role among them: it allows you to organize synsets in the form of semantic networks. For different parts of speech, generic relationships may have additional characteristics and vary in scope.
WordNet can be freely used for commercial and scientific purposes. To work with it, there are several programs, many interfaces and APIs implemented in most languages using the DICT protocol, the GoldenDict program, and others. Also, WordNet packages are present in some software repositories for GNU and Linux and their distributions.
 http://ru.akinator.com/
http://ru.akinator.com/
“Akinator” is an Internet game developed by two French programmers in 2007. Currently, December is represented in 11 languages, there is a mobile version.
The player must remember any character, and Akinator must guess it. Invented characters can be both real personalities and fictional characters from movies, fairy tales, computer games and the like.
Akinator asks 40 questions. He has two additional attempts (each with a few additional questions) in case he could not guess the player’s character’s character for the allotted 40 questions. Or, on the contrary, he can ask fewer questions if he could guess the character faster. For each question, it is proposed to choose one of five answer options: “Yes,” “Perhaps, partially,” “I don't know,” “Rather not, not really,” “No.” Akinator starts with more general questions, and each next question has a clarifying character. Thus, Akinator filters probable or inappropriate characters.
Akinator remembers how other players answered a particular question when making a guess of a certain character, and thus the corresponding roster is created for each character. If the given player answers the questions in the same way, Akinator will guess the character planned by the player. If Akinator did not guess the character, then he represents the possible characters that he assumed and offers to enter the name of the character, then remembers all the answers that were given. Thus, the number of characters known by Akinator is constantly increasing.
The power of the program in the global prevalence of the global network. Remember the old joke about the rules of the Internet? "Everything on the network has already been somewhere." This principle is used by Akinator. After all, it is used by millions of players, and the base of the magical Gene is filled with them. And Akinator's charm is very simple - the majority of users are not so erudite, so the knowledge base, even starting base, is enough to guess most of the requests.
And with complex names, heuristics methods come into play, which help Jin to teach himself, while constantly replenishing the database. As a result, for each new name, Akinator loses only to a few first players, and then, using information already known to him, adds them to each new request. Therefore, Akinator will not play with one million users, because the popularity of Gene does not fade.
The program works through the Internet using its own database, where it collects data from the Internet, organizes it, and also uses the editorial marks of the players. Thus, Akinator can guess almost any conceived items. It can be deceived, but at the same time you have to think of something that only a narrow circle of people knows about.
Comments
To leave a comment
Presentation and use of knowledge
Terms: Presentation and use of knowledge