Lecture
Positive integers 1,2,3, ┘ are called natural .
Adding to all natural numbers all fractional numbers and zero, as well as considering not only positive numbers, but also negative ones, we obtain rational numbers. Each rational number can be written as a finite decimal or infinite tidal fraction.
Irrational numbers are called infinite non-periodic fractions.
Real (or real) numbers is a collection of rational and irrational numbers.
δ - a neighborhood of the point x o is the set of points defined by the inequality 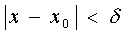 or at intervals
or at intervals 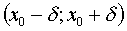 .
.
Take a set of values of the variable x and denote it by D. If according to some rule, each value of x from the set D is associated with one or several specific values of another quantity y , then they say that the quantity is a function of x . The value of x is called the argument of the function y , and the set D is the domain of definition of the function y .
The function is given by 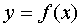 , which means that in order to find the value of y over x you need to perform some actions.
, which means that in order to find the value of y over x you need to perform some actions.
A function defined on a set of natural numbers is called a numeric sequence .
An elementary function is a function that can be defined by a single formula composed of basic elementary functions and constant using a finite number of arithmetic operations and a finite number of operations to take a function from a function.
The main elementary functions are the following functions.
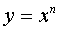 where n is a real number.
where n is a real number. 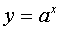 where
where 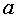 - a positive number and
- a positive number and 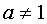 .
. 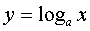 where is the base of the logarithm
where is the base of the logarithm 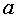 - a positive number and
- a positive number and 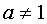 .
. 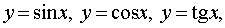

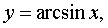
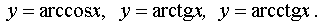
Function 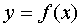 is called even if when changing the sign of any value of the argument, the value of the function does not change:
is called even if when changing the sign of any value of the argument, the value of the function does not change: 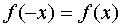 .
.
Function 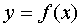 is called odd if, when changing the sign of any argument value, only the sign of the function value changes, and the absolute value of this value remains unchanged:
is called odd if, when changing the sign of any argument value, only the sign of the function value changes, and the absolute value of this value remains unchanged: 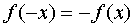 .
.
Function 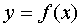 is called periodic if there is such a constant number
is called periodic if there is such a constant number 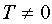 , that from adding it to any argument value, the function value does not change:
, that from adding it to any argument value, the function value does not change: 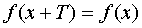 .
.
Comments
To leave a comment
Mathematical analysis. Differential calculus
Terms: Mathematical analysis. Differential calculus