Lecture
QA-system Start.
l http://start.csail.mit.edu
l Created at MIT Artificial Intelligence Laboratory in
1993 under the leadership of Boris Katz
l Universal
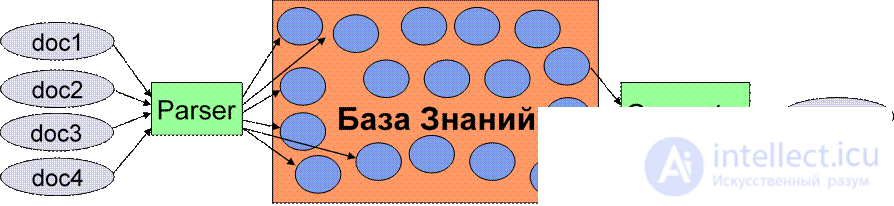
l Uses English l Knowledge Sources:
l local storage (Knowledge Base)
l internet network
l Start System Foundations: l Use specific NLP methods developed specifically for the Start system.
l The idea of creating annotations in natural languages to blocks of information
l Definition Questions:
l What is a fractal?
l Questions about the facts:
l Who invented the telegraph?
l Relationship Issues:
l What country is bigger, Russia or USA?
l List requests:
l Show me some poems by Alexander Pushkin
l ...
1. Geography
• Give me the state of Colorado.
• What's the largest city in Florida?
• Show me a map of Denmark
• List some large cities in Argentina
• Which is the Baltic Sea or the North Sea?
• Show the capital of the 2nd largest country in Asia
2. Art
• When was Beethoven born?
• Who composed the opera Semiramide?
• What movies has Dustin Hoffman been in?
3. Science and background information
• What is Jupiter's atmosphere made of?
• Why is the sky blue?
• Convert 100 dollars into Euros • How is the weather in Boston today?
• How far is Neptune from the sun?
• Show me a metro map of Moscow.
4. History and culture
• What countries speak Spanish?
• Who was the fifth president of the United States?
• What languages are spoken in the most populous country in Africa?
• How many people live on Earth?
l Consists of 3 parts:
l Ternary expressions (T-expressions)
l Syntax / semantic inference rules (S-rules)
l Catalog of words (Lexicon)
l T-expressions are expressions of the form.
<subject relationship object>
l Other T-expressions can act as an object / subject of a single T-expression.
l Adjectives, possessive pronouns, prepositions and other parts of the sentence are used to create additional T-expressions.
l The remaining attributes of the sentence (articles, tenses of verbs, adverbs, auxiliary verbs, punctuation marks, etc.) are stored in a special History structure associated with a T-expression.
“Bill surprised Hillary with his answer”
<< Bill surprise Hillary> with answer> <answer related-to Bill>
“Whom did Bill surprise with his answer?”
Question Analyzer
“Bill surprised whom with his answer?”
Parser
<< Bill surprise whom> with answer>
<answer related-to Bill>
Knowledge base
Whom = hillary
<< Bill surprise Hillary > with answer>
<answer related-to Bill>
Generator
“Bill surprised Hillary with his answer”
“Did Bill surprise with his answer?”
Question Analyzer
“Bill surprised Hillary with his answer?”
Parser
<< Bill surprise Hillary> with answer>
<answer related-to Bill>
Knowledge base
Yes!
Generator
“Yes, Bill Surprised Hillary with his answer”
l The bird ate the young snake
The snake ate the young bird
l The meaning of life
A meaningful life
l The bank of the river
The bank near the river
l Keywords:
l Loss of information about semantic connections between words.
l Texts are not compared with semantic features, but according to the statistical characteristics of keywords
l T-expressions:
l Reflect the word order in the sentence and the semantic connections between them.
l The expressive power of T-expressions is enough to write annotations in natural languages.
l Effective when indexing
What do frogs eat?
l Search based on T-expressions gave 6 answers, of which 3 are correct:
l Adult frogs eat mainly animals, including earthworms, minnows, and spiders
l One group of South American frogs feeds mainly on other frogs
l Frogs eat many other animals, including spiders, flies, and worms
l ...
What do frogs eat?
l Search based on keywords yielded 33 results, which also met the answers to the question “What eats frog?” and just the matches of the words “eat” and
“Frog”:
l Bowfins eat mainly other fish, frogs, and crayfish
l Cranes eat a variety of foods, including frogs, fishes, birds, and various small mammals.
l ...
Problem:
“Bill's answer surprised Hillary” = “Bill's surprised Hillary with his answer”
<answer surprise Hillary> << Bill surprise Hillary> with answer>
<answer related-to Bill> = <answer related-to Bill>
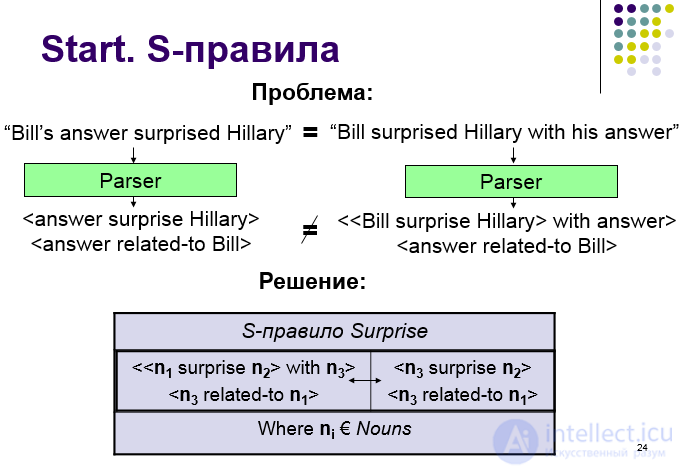
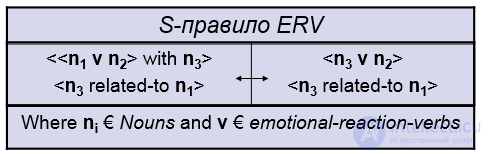
l S-rules describe linguistic variations:
l Lexical
l Synonyms
l Morphological
l Words with the same root
l syntactic
l Inversions
l Active / passive voice
l Possessive adjectives
l Also used to describe logical implications.

m 
l Some S-rules can be used in 2 directions:
l live
l when updating the knowledge base with new expressions
l in reverse
l when processing a user request
l Some S-rules apply to groups of words.
l In Lexicon contains a list of words of the language, and for each word is a list of groups to which it belongs
Comments
To leave a comment
Creating question and answer systems
Terms: Creating question and answer systems