Lecture
Combat drones are autonomous or remotely controlled devices designed to perform various combat missions. They can be of various types depending on the place of their application:
Underwater drones (unmanned underwater vehicles) are unmanned underwater vehicles capable of moving underwater. . They can be used for reconnaissance, search and destruction of underwater objects or sea mines, as well as for monitoring the marine environment. They come in a variety of sizes, from small torpedo-like underwater drones to large submersibles capable of long-duration underwater missions. Underwater drones are also equipped with various sensors such as sonars, cameras, magnetometers and other devices for detecting underwater objects, sea mines, seabed reconnaissance, etc.
surface drones(unmanned surface vehicles) are unmanned vessels that can navigate the sea surface. They can be of various sizes, ranging from small, boat-like, to large marine vessels. Surface drones are equipped with various sensors, such as radars, optical cameras, thermal imagers, hydroacoustic sensors and other devices for reconnaissance and target detection on the sea surface. They can be used for monitoring, reconnaissance, protection of waterways, as well as for the detection and destruction of enemy ships or objects. The main difference between surface and underwater drones lies in their ability to move: surface drones move on the surface of the water, while underwater drones work underwater. Each type of drone has its own unique capabilities and applications,
aerial drones : Also known as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or drones, they are designed to operate in the air. They can perform many tasks such as reconnaissance, combat, ground and air attacks, as well as monitoring and communications.
Ground drones: These are autonomous or remotely controlled robots designed to perform tasks on the ground. They can be used for a variety of purposes, including reconnaissance, target destruction, cargo transportation, combat support, and dangerous or hard-to-reach missions.
Underground combat drones are unmanned ground vehicles that are designed to perform combat missions underground. They can be used for a variety of purposes, including reconnaissance, attack, and combat support.
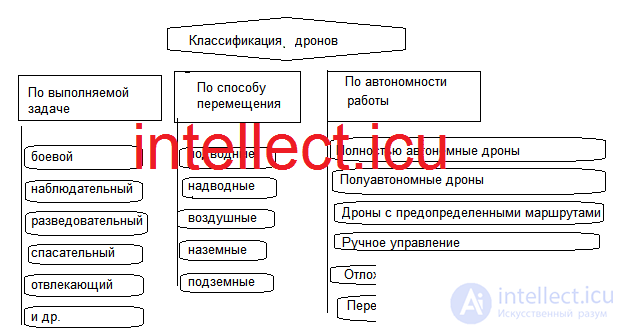
Rice. 1 Classification of intellect.icu Drones
Drones (unmanned aerial vehicles) can be divided into different types according to the degree of their autonomy. Depending on the capabilities and level of autonomy, drones can be classified as follows:
Fully Autonomous Drones: These drones are capable of performing tasks completely autonomously, without operator intervention in real time. They use various sensors, artificial intelligence and software to make decisions and complete the mission. Fully autonomous drones can plan routes, detect and avoid obstacles, perform reconnaissance and navigation without constant operator control.
Semi-autonomous drones: These drones have a certain degree of autonomy, but some tasks require the participation of an operator. For example, a drone may have autonomous navigation and flight stabilization functions, but the operator must give the command to attack the target or change the mission.
Drones with Predefined Routes: These drones follow pre-programmed routes that are determined prior to flight. They may perform tasks autonomously along a given route, but the operator may be able to change or reconfigure the route before or during flight.
Manual control: Some drones are completely dependent on the manual control of the operator. They do not have autonomous functions and perform all actions only on the operator's commands.
Switchable autonomy: Some drones may have the ability to switch between autonomous mode and manual control. This allows the operator to select the most appropriate operating mode for the specific situation.
It is important to note that the level of autonomy of a drone can vary significantly depending on its type, model and purpose. Some drones, such as reconnaissance or research drones, usually have more autonomy than combat drones, which often require more active operator participation to control the process of completing tasks.
Combat drones have been widely used in the armed forces of various countries, and their use continues to develop and increase in many areas of military operations. However, they also raise ethical and safety issues that require careful discussion and regulation.
The overall structural diagram of a combat drone (unmanned combat vehicle) may include several main components and systems.
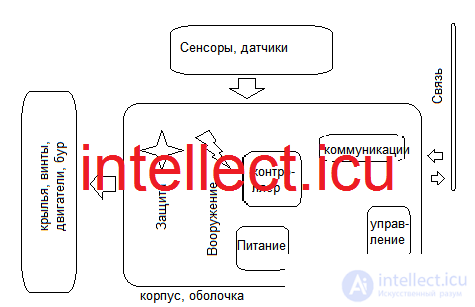
The main elements of the structural diagram of a combat drone include:
Body (shell): The body of the drone is its outer shell, which provides protection for internal components from external factors and gives the drone a certain shape and stability during flight or movement.
Wings, propellers, or motors: Depending on the type of drone, it may be equipped with wings, propellers, or motors that lift and propel the drone in the air or on the ground.
Sensors and equipment: Drones are equipped with various sensors and equipment, such as cameras, gyroscopes, accelerometers, GPS receiver, radio transmitter and other means for detection, navigation and communication.
Controller and Processor: The controller and processor are the smart brain of the drone. They process data from sensors, analyze the environment, make decisions and control the movement and behavior of the drone.
Control Systems: Control systems allow the operator to control the drone. These may include radio controls, remote controls, smartphone applications or computer software.
Power: Combat drones are usually powered by batteries or batteries. For some drones, especially long range or long missions, other power sources may be used.
Communication Systems: Various types of communication systems, such as radio or satellite, can be used to transfer data and commands between the aircraft and the operator or base station.
Defense Systems: Some combat drones may have built-in defenses against malicious attacks, hacks, or physical damage.
Armament (depending on type): Armed combat drones can be equipped with weapons such as missiles, bombs, or small arms to carry out combat missions.
These are the main elements that are usually included in the structural diagram of a combat drone. Specific characteristics and components of a drone can vary significantly depending on its purpose, type and tasks that it is designed to perform.
Combat Drone:
Surveillance Drone:
Recon Drone:
Some drones can combine the functions of observers and reconnaissance and can be used in various roles depending on the situation and mission. Each type of drone has its own advantages and applications in different situations.
Aerial drones (unmanned aerial vehicles) exist in a variety of sizes and configurations, and their performance can vary considerably depending on their purpose and application. Here are some examples of the main characteristics that can be found in aerial drones:
Flying Range: The flying range determines the maximum distance that the drone can fly from the operator or its base. For some drones, the flight range can be several kilometers or even tens of kilometers.
Max Speed: Max Speed indicates the highest speed the drone can reach while flying. Drones that are more agile and responsive can have higher speed ratings.
Flight Time: Flight time refers to the amount of time an aircraft can operate without recharging or changing the battery. The flight time can vary from a few minutes to several hours depending on the type and model of the drone.
Nose-Lift: The nose-lift determines the maximum weight the aircraft can carry while flying. This could be a camera, sensors, weapons, or other means.
Video and photo capabilities: Aerial drones can be equipped with high quality cameras and sensors that allow you to capture video and photos from the air.
Autopilot Systems: Autopilot systems allow the aircraft to perform automatic maneuvers and pre-set routes without operator intervention.
GPS navigation (or other navigation - inertial, magnetic, GLONAS,): GPS navigation capability provides accurate positioning of the drone and the ability to autonomously fly to given coordinates. use of various frequencies and noise-free channels, including with repeaters and converters of auxiliary drones
Elevator Type: Aerial drones can use various types of elevators such as propellers, propellers, jet engines, or wings in a vertical landing (VTOL).
Control and communications: Drones can be controlled by radio control, using a smartphone or tablet, as well as using satellite communications.
Safety and security: Some drones can be equipped with systems that provide protection against airborne or electronic threats, as well as emergency descent or return to base in case of loss of communication.
These are just some of the top features that aerial drones can have. The capabilities and characteristics of drones may vary depending on the manufacturer, model and purpose.

rice. examples of characteristics of aerial drones
The use of aerial drones in military intelligence is one of the most common and popular methods. Aerial drones (unmanned aerial vehicles - UAVs) provide the ability to conduct reconnaissance operations in the airspace without the need to send pilots on dangerous missions. Here are some techniques for using aerial drones in military intelligence:
Reconnaissance: Aerial drones are used to monitor the situation in enemy territory or other regions of interest. They can collect information about the movement of troops, the location of weapons, buildings and other important objects.
Search and detection of targets: Aerial drones can be used to detect enemy forces, equipment, ships and other targets. They are equipped with various sensors, such as optical cameras, IR sensors and radars, which allow them to detect targets both on the ground and in the air.
Coastline and coastal reconnaissance: Aerial drones can be used to reconnoiter the coastline and nearby sea areas. They can detect enemy ships, submarines, minefields and other objects that threaten naval forces.
Troop Movement Monitoring: Aerial drones can monitor the movement of enemy troops and convoys. This allows you to learn about their maneuvers, planned attacks and other actions, which helps to develop effective counter strategies.
Electronic intelligence: Aerial drones can perform electronic intelligence functions by listening, intercepting and analyzing enemy radio signals, which provides information about their communications, telecommunications and radio systems.
Reconnaissance in hard-to-reach areas: Aerial drones can be used to reconnoiter areas that are difficult to reach for conventional reconnaissance assets or infantry.
Performing Surrogate Attacks: Aerial drones can be used to launch attacks on specific targets by influencing the enemy without the need to send out a massive air mission.
The use of aerial drones in military intelligence requires strict adherence to international law and ethical standards. They can be very useful tools for gaining information and gaining an advantage on the battlefield, but their use must be balanced and balanced with possible consequences.
The use of aerial drones in combat plays a key role in modern armed conflicts, providing a tactical advantage and the ability to effectively perform various tasks. Here are some techniques for using aerial drones in combat:
Reconnaissance and surveillance: Aerial drones can be used to monitor the situation on the battlefield. They provide operational reconnaissance, detect enemy positions, troop movements, defensive fortifications and other important objects.
High Level Destruction: Armed Air Drones can act as fighters, attacking enemy aircraft or drones, thus providing anti-aircraft coverage for their air force.
Attack aircraft: Armed aerial drones can be used to strike at enemy ground or sea targets. They are equipped with various types of weapons such as rockets, bombs or guided missiles, allowing them to deliver accurate and effective strikes.
Performing Surrogate Attacks: Aerial drones can perform the function of surrogate attacks, drawing the attention of the enemy and diverting his attention from the main military forces.
Electronic warfare: Aerial drones can be used in electronic warfare by intercepting and jamming enemy radio signals, which leads to disruption in their communications and communication systems.
Special Operations: Aerial drones can be used in special operations such as search and rescue, interception or destruction of high priority targets.
Conducting Psychological Warfare: Aerial drones can be used to broadcast psychological information, propaganda, or relay messages to enemy personnel in order to demoralize and spread misinformation.
The use of aerial drones in combat requires strict adherence to international law and the rules of armed conflict in order to avoid violations of human rights and disproportionate use of force. This is indicated by the site https://intellect.icu. It is also necessary to ensure the security and protection of their own airspace in order to avoid possible threats from enemy drones or air forces.
The use of aerial drones in combined and complex attacks is the integration of drones with other military forces and technologies to maximize the effectiveness of attacks and achieve specific combat objectives. Here are some techniques for using aerial drones in combined and complex attacks:
Reconnaissance and combat: Aerial drones can be used for reconnaissance and detection of enemy targets and the situation on the battlefield. They can transmit real-time information to other military forces, which allows them to pinpoint targets for further attacks. At the same time, reconnaissance, observation and combat drones can be launched simultaneously or sequentially but within a short time interval, each of which complements the work of each other by performing the tasks assigned to it
Precise Strikes: Aerial drones can act as unmanned strike vehicles, striking at the precise coordinates of enemy targets. They can be used to destroy important installations, command posts, supplies, and other strategic targets.
Command and Control: Aerial drones can serve as an important means of command and control during attacks. They can provide the military leadership with information about the progress of the operation, provide communication and synchronization of the actions of various forces.
Operations in low visibility conditions: Aerial drones can be used in low visibility conditions when manned aircraft cannot perform certain missions safely. This may include night operations or missions in heavy cloud or smoke conditions.
Mass Attacks: Aerial drones can be used in mass attacks, where their coordinated action can cause significant damage to the enemy and create an advantage in battle.
Airspace Control: Aerial drones can be used to provide airspace control, identify and destroy enemy aircraft or drones, preventing them from entering their own space.
The use of air drones in combined and complex attacks, it is necessary to ensure the coordination of the actions of various armed forces and use drones, taking into account the overall strategy and tactics of a military operation. International law and ethical standards must also be observed in the use of force and the protection of the environment.
The main characteristics of underwater combat drones (unmanned underwater vehicles) may also vary depending on the type and model of the drone, its purpose and application. Here are some examples of the main characteristics of underwater combat drones:
These are the main characteristics of underwater combat drones. These characteristics can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer, model and purpose of the drone. Underwater drones can be used for various tasks, including reconnaissance, detection of underwater objects, defense of marine objects, etc.
The use of underwater drones in reconnaissance can be very effective, as they allow you to obtain information about the marine environment and underwater objects without the need to place a person under water. Here are some techniques for using underwater drones in reconnaissance:
Situation Intelligence: Underwater drones are used to monitor the situation in coastal and deep water areas. They can collect data on water temperature, salinity, currents, the presence of underwater obstacles and other parameters that are important for planning marine operations.
Search for underwater objects: Underwater drones are equipped with sensors and equipment to detect submarines, enemy ships, underwater mines and other underwater objects. This helps to identify potential threats and plan countermeasures. They can scan large areas and detect potentially dangerous objects.
Conducting raids and tracking the enemy: Underwater drones can be used to secretly enter the territory of the enemy, conduct reconnaissance raids and monitor his actions. They can also be used to eavesdrop on communications or collect other intelligence information.
Coastline reconnaissance: Underwater drones can be used to reconnoiter coastlines, shallow water areas and important marine facilities such as ports, piers or submarine cables. This allows you to ensure security during military operations and control activities on the coast. Underwater drones can also be used for reconnaissance of the coastline and important military maritime facilities, such as enemy military bases or ports, counter-intelligence.
Marine Animal Monitoring: Underwater drones can perform environmental monitoring tasks and collect information about marine animal life. This can be useful for the study and protection of vulnerable marine species and ecosystems.
Surveillance Vessels: Underwater drones can be deployed near the surface to monitor vessel movements and gather data on activity around important waterways or offshore features.
Rescue operations and underwater exploration: Underwater drones can also be used for search and rescue in case of emergencies or accidents underwater. They are able to inspect dangerous places and detect people or provide information for organizing rescue operations.
Mine Reconnaissance and Clearance: Underwater drones can help detect and clear naval mines, reducing the risk to own ships and military installations.
Rescue Operations: Armed underwater drones can also be used to rescue pilots, crews or other military personnel stranded in emergencies at sea.
Conducting large-scale operations: Military underwater drones can be used in large military operations, such as conducting anti-submarine operations or guarding sea lanes.
The use of underwater drones in military intelligence must comply with international norms and regulations in order to avoid unwanted incidents and possible violations of international law. These drones can be a very effective reconnaissance tool, but their use must be balanced and carried out according to ethical and safe standards.
The use of underwater drones in reconnaissance requires compliance with all rules and international agreements governing activities in the marine environment in order to avoid violations of sovereignty and ensure the safe use of these technologies.
The use of underwater drones in combat conditions is of great importance, as they allow for a more efficient and safe military operation under water. Here are some techniques and tactics for using underwater drones in combat:
Anti-Submarine Warfare: Underwater drones can be used to search for, locate and attack enemy submarines. They are equipped with sensors that help detect submarines and track their movement. Once detected, drones can use weapons to neutralize or destroy opponents.
Mine-Torpedo Warfare: Underwater drones can be used to place and activate underwater mines or torpedoes. They can also detect and defuse enemy mines to ensure the safety of their own ships and military installations.
Reconnaissance and Information Gathering: Armed underwater drones can perform reconnaissance missions and collect information about the enemy, their bases, important maritime installations, and enemy underwater activities.
Attacks on ground and air targets: Depending on their weapons, underwater drones can also be used to attack ground targets or air targets in coastal areas.
Electronic warfare: Underwater drones can be used to electronically jam, harass and detect enemy radio signals, which provides control over the radio frequency environment.
Perimeter Security: Underwater drones can be deployed to secure the perimeter and prevent enemy submarines and other submersibles from entering territory or waters controlled by their own forces.
Coordination of combat operations: Underwater drones can serve as an important means of communication and coordination of combat operations between different parts of the fleet or other forces involved in the operation.
The use of underwater drones in combat requires careful preparation, a high level of technical expertise, and compliance with all rules and regulations of international law, especially with regard to the use of force and environmental protection. It is also necessary to take into account possible countermeasures from the enemy, which requires constant improvement and adaptation of the tactics of using underwater drones.
The main characteristics of surface combat drones (unmanned surface vehicles) can vary significantly depending on the type and model of the drone, as well as its purpose. Here are some examples of the main characteristics of surface combat drones:
These are some of the possible characteristics of surface combat drones. The characteristics may vary significantly depending on the manufacturer, model and purpose of a particular drone. The armed forces of various countries can use different types of surface combat drones for various tasks in maritime operations.
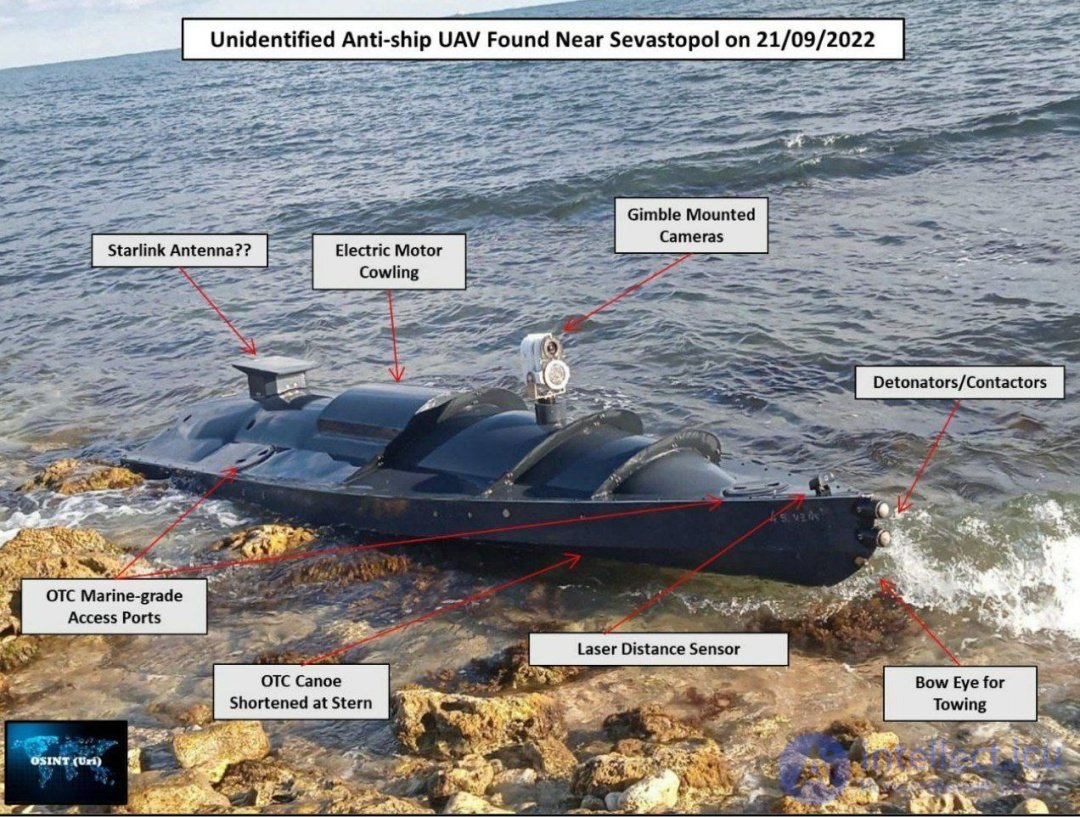

The use of surface drones (unmanned vessels) in military intelligence provides unique opportunities for collecting information about the maritime situation and the enemy. Here are some techniques for using surface drones in military intelligence:
Reconnaissance: Surface drones can be used to monitor the situation on the sea surface. They can collect data on the movement of enemy ships, the location of ports, bases, islands and other important sea objects.
Search and detection of underwater objects: Surface drones are equipped with various sensors, such as radars, sonars and optical cameras, which can detect submarines, minefields and other underwater objects of the enemy.
Coastline Reconnaissance: Surface drones can be used for coastal reconnaissance and coastline reconnaissance. They can detect enemy positions along the coast, guard important waterways, and secure military operations.
Marine Animal Monitoring: Surface drones can also be used to monitor marine wildlife and environmental conditions at sea. This can be important for protecting vulnerable species and assessing the state of the marine environment.
Surveillance Vessels: Surface drones can serve as surveillance vessels, monitoring the movement of enemy ships and other objects on the sea surface.
Anti-Submarine Warfare: Some surface drones can be used in anti-submarine warfare by detecting and following the movement of enemy submarines.
Rescue operations: Surface drones can be used to rescue the crews of downed or damaged ships.
The use of surface drones in military intelligence must comply with international norms and rules governing activities in the marine environment. You should also consider the safety of your own ships and personnel when operating with unmanned surface vehicles.
The use of surface drones in combined and complex attacks is the integration of unmanned vessels with other armed forces and means for the effective implementation of combat missions. Here are some techniques for using surface drones in such attacks:
Reconnaissance and Targeting: Surface drones can be used to reconnoiter the situation on the sea surface, detecting enemy ships, ports, bases and other objects. This information is shared with other forces to prioritize targets.
Strikes against land and sea targets: Surface drones can act as strike vehicles, using weapons against enemy land and sea targets. They can be equipped with missiles, bombs, torpedoes and other weapons.
Coordination with other forces: Surface drones can serve as a means of communication and coordination between different parts of the armed forces. They can provide information about the location of targets and the distribution of enemy forces.
Electronic warfare: Some surface drones can be used in electronic warfare by interfering with enemy electronic systems, blocking radio signals or interfering with their communications and navigation.
Performing Special Operations: Surface drones can be used in special operations, such as landing forces or sabotage operations.
Mass Attacks: Surface Drones can be used in mass attacks, where they, together with other forces, create an advantage in battle and cause significant damage to the enemy.
Conducting air defense: Some surface drones can be used in air defense, detecting and neutralizing enemy aircraft.
The successful use of surface drones in combined and complex attacks requires integration and coordination with other forces, as well as strict adherence to international law and ethical standards. Surface drone operations must also consider the safety of their own vessels and personnel, as well as minimize risks to civilians and the environment.
The main characteristics of ground combat drones (unmanned ground vehicles) may vary depending on the type and model of the drone, its purpose and the type of combat missions it performs. Here are some examples of the main characteristics of ground combat drones:
These are examples of the characteristics of ground combat drones. Each type of drone can have its own unique characteristics that determine its ability to perform various combat missions on the ground.
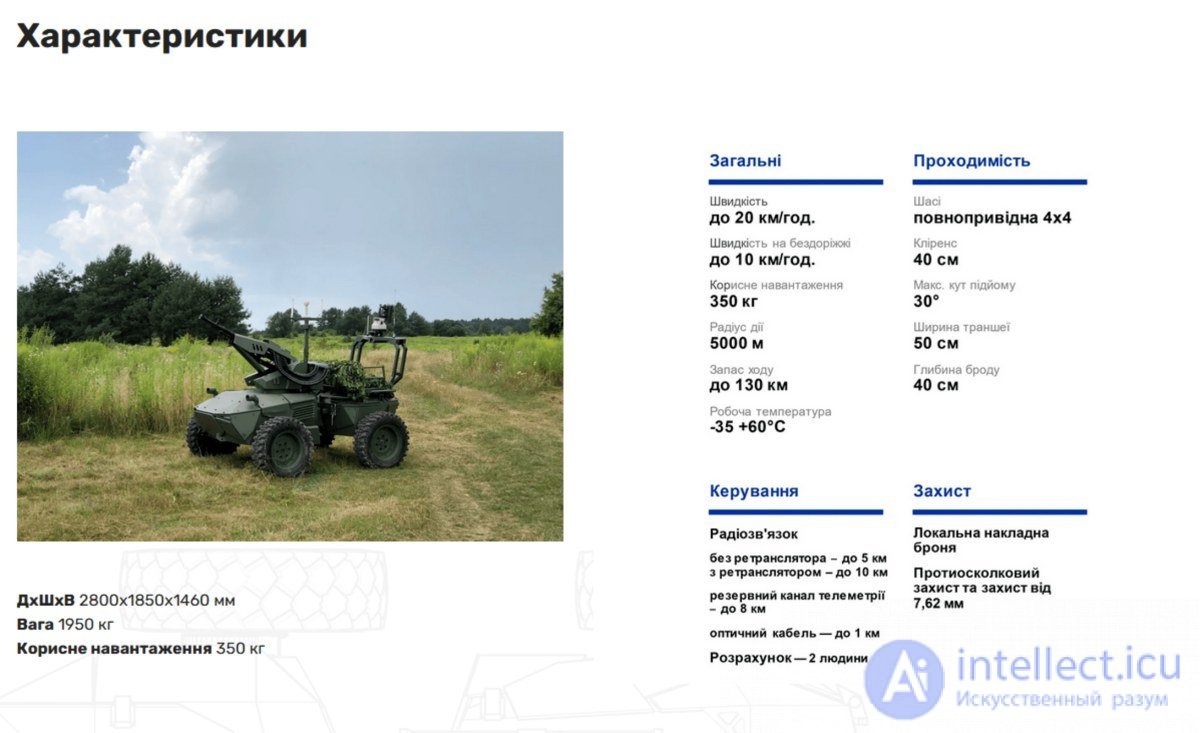
Rice. an example of the characteristics of a ground drone is Ironclad.
The use of ground drones (unmanned ground vehicles) in military intelligence provides a wide range of opportunities for collecting intelligence information on land. Here are some techniques for using ground drones in military intelligence:
Reconnaissance: Ground drones are used to monitor the situation on land. They can move around the area, collect information about the area, detect and analyze objects and structures, and monitor the movement of enemy forces.
Search and detection of targets: Ground drones are equipped with various sensors, such as optical cameras, thermal imagers and radars, which can detect enemy equipment, manpower, tanks, missile launchers and other targets on the ground.
Artillery Reconnaissance: Ground drones can be used to determine the coordinates of enemy artillery positions and accurately target artillery fire.
Terrain Mapping and Survey: Ground-based drones can be used to create terrain maps, including hard-to-reach or dangerous areas, making it easier to plan military operations.
Border control and security of facilities: Ground drones can be used to control the border or secure military installations such as bases, warehouses or other critical places.
Hazard Reconnaissance: Ground drones can be used in hazardous situations where human presence may be risky or impossible, such as in areas with chemical or radioactive contamination.
Special Operations: Ground drones can be used in special operations such as pre-invasion reconnaissance, night operations, or concealment of one's own activities.
Electronic Reconnaissance: Some ground drones can be used for electronic reconnaissance by listening, intercepting and analyzing enemy radio signals.
The use of ground drones in military intelligence must comply with international norms and rules, especially with regard to the inviolability of the territories of other states and the protection of human rights. You also need to consider the security of your own military and minimize the risks to the civilian population.
The use of ground drones in combined and complex attacks provides an opportunity to integrate them with other armed forces and technologies to implement joint combat operations. Here are some techniques for using ground drones in such attacks:
Reconnaissance and target detection: Ground drones can be used in reconnaissance and target detection on the ground. They can provide operational intelligence and information on the location of enemy forces and installations.
Force Coordination: Ground drones can serve as an important means of communication and coordination between different military forces on the battlefield. They can provide information about the location of their forces and the enemy, as well as help synchronize actions for the effective execution of tasks.
Precise Strikes: Ground drones can act as strike machines, using their weapons against enemy targets. They can be equipped with rockets, grenades, or other types of weapons for accurate and effective strikes.
Border control: Ground-based drones can be deployed to control the border and detect illegal border crossings.
Conducting Special Operations: Ground drones can be used in special operations such as pre-invasion reconnaissance, infiltrating captured territories, or performing sabotage missions.
Unmanned Combat Teams: Ground drones can be combined into unmanned combat teams, working in combination with infantry or other forces to increase their effectiveness in combat.
Electronic warfare: Some ground-based drones can be used in electronic warfare, chasing and jamming enemy radio signals, which provides control over the radio frequency environment.
Rescue operations: Ground drones can be used for rescue operations, search and rescue of people in dangerous conditions.
The successful use of ground drones in combined and complex attacks requires coordination and integration with other military forces, as well as adherence to international law and ethical standards. Ground drone operations must also consider the safety of their own military and minimize risks to the civilian population.
Underground combat drones (unmanned underground vehicles) are special unmanned ground devices designed to perform combat missions underground or inside buildings. Here are some examples of the main characteristics of underground combat drones:
These are some examples of the characteristics of underground combat drones. Specifications can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer, model and purpose of a particular drone. Underground drones can be used to perform various combat missions, such as reconnaissance, threat neutralization, rescue operations, and others.
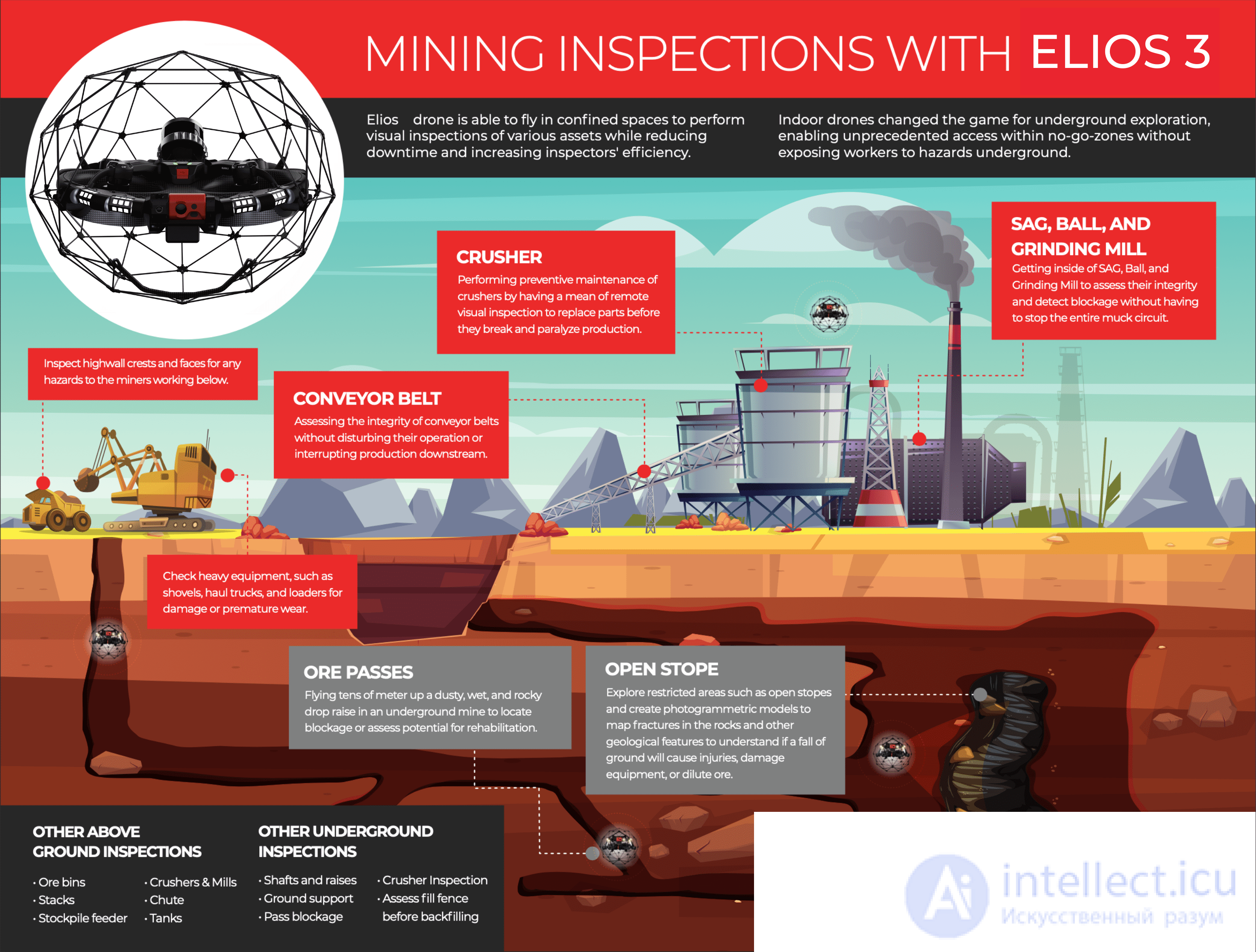
To date, the use of underground drones (unmanned ground vehicles) in military intelligence is not yet as widespread as the use of air or ground drones. However, with the development of technology and the emergence of more advanced underground drones, the possibilities of their use in military intelligence can expand significantly. Here are some potential applications of underground drones in military intelligence:
Reconnaissance in hard-to-reach places: Underground drones can be used for reconnaissance and gathering information in hard-to-reach places, such as underground tunnels, sewers, collapsed buildings and other objects that are difficult to access by foot reconnaissance or other means.
Detection and marking of mines and traps: Underground drones can be used to detect and mark mines and traps on the ground, thus avoiding dangerous situations for soldiers and marking dangerous areas on the map.
Reconnaissance in tunnels and underground structures: Underground drones can be used to explore and reconnoiter enemy tunnels and underground structures, detect hidden objects or secret bases.
Investigation of suspicious objects: Underground drones can be used to investigate suspicious objects or areas in the territory, which helps to reconnoiter possible threats and dangers.
Undercover Intelligence Gathering: Underground drones can act as covert spies, gathering information about an enemy undercover and remaining undetected.
Electronic intelligence: Some underground drones can be used in electronic intelligence, intercepting enemy radio signals and analyzing them for information on communications and communications.
Rescue Operations: In case of emergencies or accidents, underground drones can be used to search and rescue people in hard-to-reach places.
The use of underground drones in military intelligence may face technical and technological challenges, such as the reliability of communication and navigation underground. It is also necessary to comply with international law and ethical standards when using such technologies.
The use of underground drones in combined and complex attacks is the integration of these unmanned ground vehicles with other military forces and technologies to perform a variety of combat missions. Here are some techniques for using underground drones in such attacks:
Reconnaissance and Information Gathering: Underground drones can be used for covert reconnaissance and gathering information about the battlefield, terrain, and the deployment of enemy forces and facilities.
Target Acquisition and Destruction: Underground drones can act as reconnaissance vehicles to locate enemy targets and transmit coordinates for precision strikes by other forces.
Border control and facility protection: Underground drones can be used for border control, detection of intruders, and protection of important facilities such as military bases or critical infrastructure facilities.
Mining and Enemy Slowdown: Underground drones can be used to place mines and slow down the advance of enemy forces in an area.
Electronic Reconnaissance and Communication Disruption: Underground drones can be used in electronic reconnaissance, intercepting or disrupting enemy communications and radio signals.
Underground tunnel monitoring: In areas where underground tunnels are used to move enemy forces, underground drones can perform the function of monitoring and detecting illegal tunnels.
Rescue and evacuation: Underground drones can be used to rescue and evacuate the injured or provide assistance in erratic situations.
Infantry Control and Support: Underground drones can serve as an auxiliary force for infantry, providing them with additional means of surveillance and detection.
The successful use of underground drones in combined and complex attacks requires coordination and integration with other military forces, as well as compliance with international law and ethical standards. Operations with underground drones must also consider the safety of their own military and minimize the risks to the civilian population.
Autonomous Mode: In this mode, the drone is able to perform tasks autonomously without the operator's continuous supervision. It uses embedded algorithms and artificial intelligence to make decisions and complete the mission.
Position Hold: This mode allows the aircraft to automatically hold a given position in space, which is especially useful when aiming a weapon or taking precise measurements.
Self-Destruct: Some combat drones can be equipped with a self-destruct feature that allows them to be destroyed if captured or in the event of falling into enemy hands.
Stealth Mode: In this mode, the drone uses various methods to reduce radar and infrared visibility to reduce its visibility to the enemy.
Blast Wave Mode: This mode involves launching multiple drones at the same time, which perform coordinated attacks or reconnaissance.
"Flight Instability" Mode: Some drones can be capable of flight instability, making them more difficult for enemies to see and more maneuverable.
These are just some examples of the special operating modes of combat drones. Each type of drone can have its own unique features and capabilities that allow them to successfully perform various combat missions and be used in various scenarios.
Anti-drone equipment and facilities are designed to counter unwanted and potentially dangerous drones. They are being developed to detect, identify and neutralize aerial drones that can pose a threat to the security and privacy of various places and activities.
Anti-drone equipment and facilities may include various technologies and systems:
Drone Detection: This includes radars, RF scanners, optical and infrared sensors that can detect the presence of drones on the ground or in the air.
Identification and classification: Specialized data processing algorithms and drone databases can be used to determine the characteristics and types of drones.
Neutralization: This includes various countermeasures such as blocking radio communications or drone control, jamming, electronic interference, using interceptor drones or controlled networks to take over the drone.
Physical Means: These could be special weapons or systems that can physically disable drones, such as nets, lasers, or other means.
Software: Software solutions for anti-drone equipment control, data analysis and decision making play an important role.
Comments
To leave a comment
Warfare
Terms: Warfare